Multiple roles for the C-terminal domain of eIF5 in translation initiation complex assembly and GTPase activation
- PMID: 11331597
- PMCID: PMC125443
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2326
Multiple roles for the C-terminal domain of eIF5 in translation initiation complex assembly and GTPase activation
Abstract
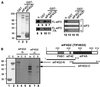
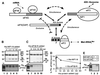
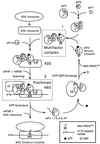
eIF5 stimulates the GTPase activity of eIF2 bound to Met-tRNA(i)(Met), and its C-terminal domain (eIF5-CTD) bridges interaction between eIF2 and eIF3/eIF1 in a multifactor complex containing Met-tRNA(i)(Met). The tif5-7A mutation in eIF5-CTD, which destabilizes the multifactor complex in vivo, reduced the binding of Met-tRNA(i)(Met) and mRNA to 40S subunits in vitro. Interestingly, eIF5-CTD bound simultaneously to the eIF4G subunit of the cap-binding complex and the NIP1 subunit of eIF3. These interactions may enhance association of eIF4G with eIF3 to promote mRNA binding to the ribosome. In vivo, tif5-7A eliminated eIF5 as a stable component of the pre-initiation complex and led to accumulation of 48S complexes containing eIF2; thus, conversion of 48S to 80S complexes is the rate-limiting defect in this mutant. We propose that eIF5-CTD stimulates binding of Met-tRNA(i)(Met) and mRNA to 40S subunits through interactions with eIF2, eIF3 and eIF4G; however, its most important function is to anchor eIF5 to other components of the 48S complex in a manner required to couple GTP hydrolysis to AUG recognition during the scanning phase of initiation.
Figures





References
-
- Asano K., Phan,L., Anderson,J. and Hinnebusch,A.G. (1998) Complex formation by all five homologues of mammalian translation initiation factor 3 subunits from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 18573–18585. - PubMed
-
- Benne R. and Hershey,J.W.B. (1978) The mechanism of action of protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes. J. Biol. Chem., 253, 3078–3087. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti A. and Maitra,U. (1991) Function of eukaryotic initiation factor 5 in the formation of an 80S ribosomal polypeptide chain initiation complex. J. Biol. Chem., 266, 14039–14045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

