SRbeta coordinates signal sequence release from SRP with ribosome binding to the translocon
- PMID: 11331598
- PMCID: PMC125438
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.9.2338
SRbeta coordinates signal sequence release from SRP with ribosome binding to the translocon
Abstract
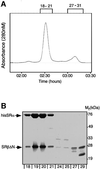
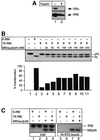
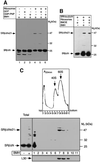
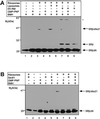
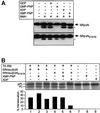
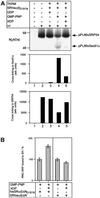
Protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane is regulated by three GTPases, the 54 kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) and the alpha- and beta-subunits of the SRP receptor (SR). Using a soluble form of SR and an XTP-binding mutant of SRbeta, we show that SRbeta is essential for protein translocation across the ER membrane. SRbeta can be cross-linked to a 21 kDa ribosomal protein in its empty and GDP-bound state, but not when GTP is bound. GTP binding to SRbeta is required to induce signal sequence release from SRP. This is achieved by the presence of the translocon, which changes the interaction between the 21 kDa ribosomal protein and SRbeta and thereby allows SRbeta to bind GTP. We conclude that SRbeta coordinates the release of the signal sequence from SRP with the presence of the translocon.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ribosome regulates the GTPase of the beta-subunit of the signal recognition particle receptor.J Cell Biol. 1999 Aug 23;146(4):723-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.4.723. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10459008 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation by the ribosome of the GTPase of the signal-recognition particle during protein targeting.Nature. 1996 May 16;381(6579):248-51. doi: 10.1038/381248a0. Nature. 1996. PMID: 8622769
-
The bacterial SRP receptor, SecA and the ribosome use overlapping binding sites on the SecY translocon.Traffic. 2011 May;12(5):563-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01167.x. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21255212
-
A structural step into the SRP cycle.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Jul;53(2):357-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04139.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15228518 Review.
-
Structure, function and evolution of the signal recognition particle.EMBO J. 2003 Jul 15;22(14):3479-85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg337. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12853463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predominant membrane localization is an essential feature of the bacterial signal recognition particle receptor.BMC Biol. 2009 Nov 13;7:76. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-76. BMC Biol. 2009. PMID: 19912622 Free PMC article.
-
A trans-membrane segment inside the ribosome exit tunnel triggers RAMP4 recruitment to the Sec61p translocase.J Cell Biol. 2009 Jun 1;185(5):889-902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200807066. Epub 2009 May 25. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19468070 Free PMC article.
-
SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The Role of the Signal Recognition Particle in Protein Targeting and mRNA Protection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 11;22(12):6284. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126284. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34208095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A ribosome-associated chaperone enables substrate triage in a cotranslational protein targeting complex.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 17;11(1):5840. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19548-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33203865 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a novel GTPase priming step in the SRP protein targeting pathway.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6724-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.23.6724. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11726508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacher G., Lütcke,H., Jungnickel,B., Rapoport,T.A. and Dobberstein,B. (1996) Regulation by the ribosome of the GTPase of the signal recognition particle during protein targeting. Nature, 381, 248–251. - PubMed
-
- Beckman R.D., Bubeck,R., Grassucci,P., Penczek,A., Verschoor,J., Blobel,G. and Frank,J. (1997) Alignment of conduits for the nascent polypeptide chain in the ribosome–Sec61 complex. Science, 278, 2123–2126. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein H.D., Poritz,M.A., Strub,K., Hoben,P.J., Brenner,S. and Walter,P. (1989) Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature, 340, 482–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

