Negative regulation of Gcn4 and Msn2 transcription factors by Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinase
- PMID: 11331604
- PMCID: PMC312682
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.867501
Negative regulation of Gcn4 and Msn2 transcription factors by Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinase
Abstract
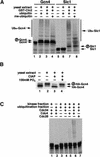
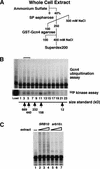
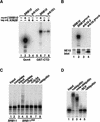
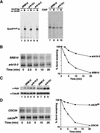
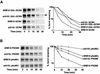
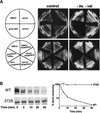
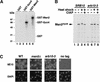
The budding yeast transcriptional activator Gcn4 is rapidly degraded in an SCF(Cdc4)-dependent manner in vivo. Upon fractionation of yeast extracts to identify factors that mediate Gcn4 ubiquitination, we found that Srb10 phosphorylates Gcn4 and thereby marks it for recognition by SCF(Cdc4) ubiquitin ligase. Srb10 is a physiological regulator of Gcn4 stability because both phosphorylation and turnover of Gcn4 are diminished in srb10 mutants. Gcn4 is almost completely stabilized in srb10Delta pho85Delta cells, or upon mutation of all Srb10 phosphorylation sites within Gcn4, suggesting that the Pho85 and Srb10 cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) conspire to limit the accumulation of Gcn4. The multistress response transcriptional regulator Msn2 is also a substrate for Srb10 and is hyperphosphorylated in an Srb10-dependent manner upon heat-stress-induced translocation into the nucleus. Whereas Msn2 is cytoplasmic in resting wild-type cells, its nuclear exclusion is partially compromised in srb10 mutant cells. Srb10 has been shown to repress a subset of genes in vivo, and has been proposed to inhibit transcription via phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. We propose that Srb10 also inhibits gene expression by promoting the rapid degradation or nuclear export of specific transcription factors. Simultaneous down-regulation of both transcriptional regulatory proteins and RNA polymerase may enhance the potency and specificity of transcriptional inhibition by Srb10.
Figures

Comment in
-
Transcriptional activation: risky business.Genes Dev. 2001 May 1;15(9):1045-50. doi: 10.1101/gad.896501. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11331599 Review.
Similar articles
-
Degradation of the transcription factor Gcn4 requires the kinase Pho85 and the SCF(CDC4) ubiquitin-ligase complex.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Mar;11(3):915-27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.3.915. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10712509 Free PMC article.
-
GAL4 is regulated by the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme-associated cyclin-dependent protein kinase SRB10/CDK8.Mol Cell. 1999 May;3(5):673-8. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80360-3. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10360183
-
A transcriptional autoregulatory loop for KIN28-CCL1 and SRB10-SRB11, each encoding RNA polymerase II CTD kinase-cyclin pair, stimulates the meiotic development of S. cerevisiae.Yeast. 2000 Jun 30;16(9):829-46. doi: 10.1002/1097-0061(20000630)16:9<829::AID-YEA581>3.0.CO;2-6. Yeast. 2000. PMID: 10861906
-
Controlling transcription by destruction: the regulation of yeast Gcn4p stability.Curr Genet. 2003 Oct;44(1):8-18. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0422-3. Epub 2003 Jul 9. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 14508604 Review.
-
Transcriptional activation: risky business.Genes Dev. 2001 May 1;15(9):1045-50. doi: 10.1101/gad.896501. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11331599 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin Association of Gcn4 Is Limited by Post-translational Modifications Triggered by its DNA-Binding in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 Dec;204(4):1433-1445. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.194134. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27770033 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator Undergoes a Compositional Change during Transcriptional Activation.Mol Cell. 2016 Nov 3;64(3):443-454. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.015. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27773675 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of the Sef1 transcription factor controls the virulence of Candida albicans in its mammalian host.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1002956. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002956. Epub 2012 Nov 1. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23133381 Free PMC article.
-
CTD kinase I is involved in RNA polymerase I transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Nov 1;32(19):5851-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh927. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15520468 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 positively cooperates with Mediator to promote thyroid hormone receptor-dependent transcriptional activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 May;30(10):2437-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01541-09. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20231357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Beck T, Hall MN. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999;402:689–692. - PubMed
-
- Carlson M. Genetics of transcriptional regulation in yeast: Connections to the RNA polymerase II CTD. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Carr SA, Huddleston MJ, Annan RS. Selective detection and sequencing of phosphopeptides at the femtomole level by mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1996;239:180–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
