Subcellular localization of the Snf1 kinase is regulated by specific beta subunits and a novel glucose signaling mechanism
- PMID: 11331606
- PMCID: PMC312685
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.879301
Subcellular localization of the Snf1 kinase is regulated by specific beta subunits and a novel glucose signaling mechanism
Abstract
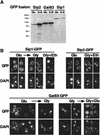
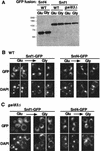
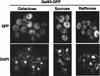
The Snf1/AMP-activated protein kinase family has broad roles in transcriptional, metabolic, and developmental regulation in response to stress. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Snf1 is required for the response to glucose limitation. Snf1 kinase complexes contain the alpha (catalytic) subunit Snf1, one of the three related beta subunits Gal83, Sip1, or Sip2, and the gamma subunit Snf4. We present evidence that the beta subunits regulate the subcellular localization of the Snf1 kinase. Green fluorescent protein fusions to Gal83, Sip1, and Sip2 show different patterns of localization to the nucleus, vacuole, and/or cytoplasm. We show that Gal83 directs Snf1 to the nucleus in a glucose-regulated manner. We further identify a novel signaling pathway that controls this nuclear localization in response to glucose phosphorylation. This pathway is distinct from the glucose signaling pathway that inhibits Snf1 kinase activity and responds not only to glucose but also to galactose and sucrose. Such independent regulation of the localization and the activity of the Snf1 kinase, combined with the distinct localization of kinases containing different beta subunits, affords versatility in regulating physiological responses.
Figures





References
-
- Alepuz PM, Cunningham KW, Estruch F. Glucose repression affects ion homeostasis in yeast through the regulation of the stress-activated ENA1 gene. Mol Microbiol. 1997;26:91–98. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafi K, Farazi TA, Gordon JI. A role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae fatty acid activation protein 4 in regulating protein N-myristoylation during entry into stationary phase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:25864–25874. - PubMed
-
- Beck T, Hall MN. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999;402:689–692. - PubMed
-
- Carlson M. Glucose repression in yeast. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:202–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
