Glutamate antagonists limit tumor growth
- PMID: 11331750
- PMCID: PMC33475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.091113598
Glutamate antagonists limit tumor growth
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001 Jul 17;98(15):8921
Abstract
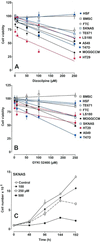
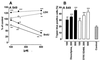
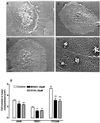
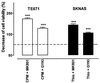
Neuronal progenitors and tumor cells possess propensity to proliferate and to migrate. Glutamate regulates proliferation and migration of neurons during development, but it is not known whether it influences proliferation and migration of tumor cells. We demonstrate that glutamate antagonists inhibit proliferation of human tumor cells. Colon adenocarcinoma, astrocytoma, and breast and lung carcinoma cells were most sensitive to the antiproliferative effect of the N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist dizocilpine, whereas breast and lung carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, and neuroblastoma cells responded most favorably to the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate antagonist GYKI52466. The antiproliferative effect of glutamate antagonists was Ca(2+) dependent and resulted from decreased cell division and increased cell death. Morphological alterations induced by glutamate antagonists in tumor cells consisted of reduced membrane ruffling and pseudopodial protrusions. Furthermore, glutamate antagonists decreased motility and invasive growth of tumor cells. These findings suggest anticancer potential of glutamate antagonists.
Figures

Comment in
-
Glutamate antagonists: deadly liaisons with cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 May 22;98(11):5947-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121179198. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11371628 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

