Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein a1 binds to the 3'-untranslated region and mediates potential 5'-3'-end cross talks of mouse hepatitis virus RNA
- PMID: 11333880
- PMCID: PMC114904
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5009-5017.2001
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein a1 binds to the 3'-untranslated region and mediates potential 5'-3'-end cross talks of mouse hepatitis virus RNA
Abstract
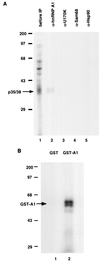
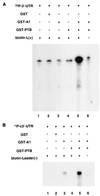
The 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) RNA regulates the replication of and transcription from the viral RNA. Several host cell proteins have previously been shown to interact with this regulatory region. By immunoprecipitation of UV-cross-linked cellular proteins and in vitro binding of the recombinant protein, we have identified the major RNA-binding protein species as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1). A strong hnRNP A1-binding site was located 90 to 170 nucleotides from the 3' end of MHV RNA, and a weak binding site was mapped at nucleotides 260 to 350 from the 3' end. These binding sites are complementary to the sites on the negative-strand RNA that bind another cellular protein, polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB). Mutations that affect PTB binding to the negative strand of the 3'-UTR also inhibited hnRNP A1 binding on the positive strand, indicating a possible relationship between these two proteins. Defective-interfering RNAs containing a mutated hnRNP A1-binding site have reduced RNA transcription and replication activities. Furthermore, hnRNP A1 and PTB, both of which also bind to the complementary strands at the 5' end of MHV RNA, together mediate the formation of an RNP complex involving the 5'- and 3'-end fragments of MHV RNA in vitro. These studies suggest that hnRNP A1-PTB interactions provide a molecular mechanism for potential 5'-3' cross talks in MHV RNA, which may be important for RNA replication and transcription.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein binds to the leader RNA of mouse hepatitis virus and serves as a regulator of viral transcription.J Virol. 1999 Jan;73(1):772-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.772-777.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9847386 Free PMC article.
-
Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein binds to the complementary strand of the mouse hepatitis virus 3' untranslated region, thereby altering RNA conformation.J Virol. 1999 Nov;73(11):9110-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.11.9110-9116.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10516017 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular protein hnRNP-A1 interacts with the 3'-end and the intergenic sequence of mouse hepatitis virus negative-strand RNA to form a ribonucleoprotein complex.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;440:227-34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5331-1_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9782285
-
[Structure and function of the non-coding regions of hepatitis C viral RNA].Postepy Biochem. 2006;52(1):62-71. Postepy Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16869303 Review. Polish.
-
Functional interactions between polypyrimidine tract binding protein and PRI peptide ligand containing proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Aug 15;44(4):1058-65. doi: 10.1042/BST20160080. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27528752 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic interactions between an essential 3' cis-acting RNA pseudoknot, replicase gene products, and the extreme 3' end of the mouse coronavirus genome.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(3):1214-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01690-07. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18032506 Free PMC article.
-
5'- and 3'-noncoding regions in flavivirus RNA.Adv Virus Res. 2003;59:177-228. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(03)59006-6. Adv Virus Res. 2003. PMID: 14696330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-RNA and RNA-protein interactions in coronavirus replication and transcription.RNA Biol. 2011 Mar-Apr;8(2):237-48. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.2.14991. Epub 2011 Mar 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21378501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRES-driven translation is stimulated separately by the FMDV 3'-NCR and poly(A) sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Oct 15;30(20):4398-405. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf569. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12384586 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nucleotides immediately flanking the transcription-regulating sequence core in coronavirus subgenomic mRNA synthesis.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(4):2506-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.4.2506-2516.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15681451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bothwell A L, Ballard D W, Philbrick W M, Lindwall G, Maher S E, Bridgett M M, Jamison S F, Garcia-Blanco M A. Murine polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Purification, cloning, and mapping of the RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:24657–24663. - PubMed
-
- Cartegni L, Maconi M, Morandi E, Cobianchi F, Riva S, Biamonti G. hnRNP A1 selectively interacts through its Gly-rich domain with different RNA-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 1996;259:337–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

