Efficient infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes with purified human and woolly monkey hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 11333889
- PMCID: PMC114913
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5084-5089.2001
Efficient infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes with purified human and woolly monkey hepatitis B virus
Abstract
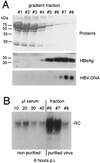
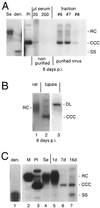
The Asian tree shrew, Tupaia belangeri, has been proposed as a novel animal model for studying hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Here, we describe a protocol for efficient and reproducible infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes with HBV. We report that human serum interferes with HBV binding to the hepatocytes, thus limiting the maximum multiplicity of infection. Purification of HBV virions by gradient sedimentation greatly enhances virus binding and infectivity. Covalently closed circular DNA was clearly detectable by Southern blot analysis and newly synthesized single-stranded HBV DNA was visible 2 weeks postinoculation. Primary tupaia hepatocytes are also susceptible to infection with the recently discovered woolly monkey hepatitis B virus (WMHBV) but not to woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Compared to HBV, WMHBV replicated at a higher rate with single-stranded DNA detectable within the first week postinoculation. Primary tupaia hepatocytes should represent a useful system for studying early steps of HBV and WMHBV infection.
Figures

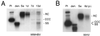

Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) virion and covalently closed circular DNA formation in primary tupaia hepatocytes and human hepatoma cell lines upon HBV genome transduction with replication-defective adenovirus vectors.J Virol. 2001 Feb;75(3):1104-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.3.1104-1116.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11152483 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus infection of tupaia hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo.Hepatology. 1996 Jul;24(1):1-5. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240101. Hepatology. 1996. PMID: 8707245
-
Hepatitis B virus mutations associated with fulminant hepatitis induce apoptosis in primary Tupaia hepatocytes.Hepatology. 2005 Feb;41(2):247-56. doi: 10.1002/hep.20553. Hepatology. 2005. PMID: 15660384
-
Entry of hepatitis B virus: mechanism and new therapeutic target.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2010 Aug;58(4):301-7. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 May 31. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2010. PMID: 20570056 Review.
-
Small animal model systems for studying hepatitis B virus replication and pathogenesis.Semin Liver Dis. 2006 May;26(2):181-91. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-939760. Semin Liver Dis. 2006. PMID: 16673296 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection and occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri chinensis).Virol J. 2015 Feb 13;12:26. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0256-x. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 25889678 Free PMC article.
-
A Chimeric Humanized Mouse Model by Engrafting the Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocyte-Like Cell for the Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 8;9:908. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00908. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29867819 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse interleukin-7 mRNA transcripts in Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis).PLoS One. 2014 Jun 19;9(6):e99859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099859. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24945249 Free PMC article.
-
Productive HBV infection of well-differentiated, hNTCP-expressing human hepatoma-derived (Huh7) cells.Virol Sin. 2017 Dec;32(6):465-475. doi: 10.1007/s12250-017-3983-x. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Virol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28971350 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection in Tupaia belangeri.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):303-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01448-09. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19846521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldrich C E, Coates L, Wu T T, Newbold J, Tennant B C, Summers J, Seeger C, Mason W S. In vitro infection of woodchuck hepatocytes with woodchuck hepatitis virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989;172:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Darai G, Schwaiger A, Komitowski D, Munk K. Experimental infection of Tupaia belangeri (tree shrews) with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Infect Dis. 1978;137:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Dienstag J L, Schiff E R, Wright T L, Perrillo R P, Hann H W, Goodman Z, Crowther L, Condreay L D, Woessner M, Rubin M, Brown N A. Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1256–1263. - PubMed
-
- Fowler E, Raab-Traub N, Hester S. Purification of biologically active Epstein-Barr virus by affinity chromatography and nonionic density gradient centrifugation. J Virol Methods. 1985;11:59–74. - PubMed
-
- Galle P R, Hagelstein J, Kommerell B, Volkmann M, Schranz P, Zentgraf H. In vitro experimental infection of primary human hepatocytes with hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:664–673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

