Determination of essential amino acids involved in the CD4-independent tropism of the X4 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 m7NDK isolate: role of potential N glycosylations in the C2 and V3 regions of gp120
- PMID: 11333929
- PMCID: PMC114953
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5425-5428.2001
Determination of essential amino acids involved in the CD4-independent tropism of the X4 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 m7NDK isolate: role of potential N glycosylations in the C2 and V3 regions of gp120
Abstract
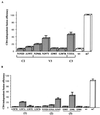
Seven mutations in the C2, V3, and C3 regions of gp120 are implicated in the tropism of the first CD4-independent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate, m7NDK. Site-directed mutagenesis revealed that three amino acids are essential to maintain this tropism, one in the C2 region and two in the V3 loop. Two mutations implied N glycosylation modifications.
Figures
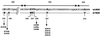

References
-
- Berger E A, Murphy P M, Farber J M. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:657–700. - PubMed
-
- Catasti P, Bradbury E M, Gupta G. Structure and polymorphism of HIV-1 third variable loops. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:8236–8242. - PubMed
-
- Catasti P, Fontenot J D, Bradbury E M, Gupta G. Local and global structural properties of the HIV-MN V3 loop. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2224–2232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

