Regulation of gap junctional communication by a pro-inflammatory cytokine in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-expressing but not cystic fibrosis airway cells
- PMID: 11337375
- PMCID: PMC1891964
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64133-8
Regulation of gap junctional communication by a pro-inflammatory cytokine in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-expressing but not cystic fibrosis airway cells
Abstract
Airway inflammation is orchestrated by cell-cell interactions involving soluble mediators and cell adhesion molecules. Alterations in the coordination of the multicellular process of inflammation may play a major role in the chronic lung disease state of cystic fibrosis (CF). The aim of this study was to determine whether direct cell-cell interactions via gap junctional communication is affected during the inflammatory response of the airway epithelium. We have examined the strength of intercellular communication and the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) in normal (non-CF) and CF human airway cell lines stimulated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). TNF-alpha induced maximal translocation of NF-kappaB into the nucleus of non-CF as well as CF airway cells within 20 minutes. In non-CF cells, TNF-alpha progressively decreased the extent of intercellular communication. In contrast, gap junctional communication between CF cells exposed to TNF-alpha remained unaltered. CF results from mutations of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Interestingly, transfer of wild-type CFTR into CF cells by adenovirus-mediated infection was associated with the recovery of TNF-alpha-induced uncoupling. These results suggest that expression of functional CFTR is necessary for regulation of gap junctional communication by TNF-alpha. Gap junction channels close during the inflammatory response, therefore limiting the intercellular diffusion of signaling molecules, and thereby the recruitment of neighboring cells. Defects in this mechanism may contribute to the excessive inflammatory response of CF airway epithelium.
Figures
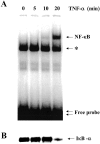
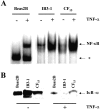

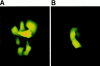


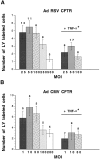
Comment in
-
Cytokine regulation of gap junction connectivity: an open-and-shut case or changing partners at the Nexus?Am J Pathol. 2001 May;158(5):1565-9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64110-7. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11337352 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Welsh MJ, Tsui L-C, Boat TM, Beaudet AL: Cystic fibrosis. ed 7 Scriver CR Beaudet AL Sly WS Valle D eds. The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease, 1995, :pp 3799-3876 McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Schwiebert EM, Benos DJ, Egan ME, Stutts MJ, Guggino WB: CFTR is a conductance regulator as well as a chloride channel. Physiol Rev 1999, 79:S145-S166 - PubMed
-
- Tosi MF, Stark JM, Smith CW, Hamedani A, Gruenert DC, Infeld MD: Induction of ICAM-1 expression on human airway epithelial cells by inflammatory cytokines: effects on neutrophil-epithelial cell adhesion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1992, 7:214-221 - PubMed
-
- Bonfield TM, Panuska JR, Konstan MW, Hilliard KA, Hilliard JB, Ghnaim H, Berger M: Inflammatory cytokines in cystic fibrosis lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995, 152:2111-2118 - PubMed
-
- Noah TL, Black HR, Cheng PW, Wood RE, Leigh MW: Nasal and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cytokines in early cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis 1997, 175:638-647 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

