ABC of hypertension. Blood pressure measurement. Part III-automated sphygmomanometry: ambulatory blood pressure measurement
- PMID: 11337446
- PMCID: PMC1120240
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1110
ABC of hypertension. Blood pressure measurement. Part III-automated sphygmomanometry: ambulatory blood pressure measurement
Figures

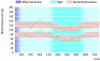
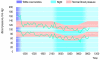


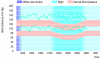

References
-
- O'Brien E, Petrie J, Littler WA, de Swiet M, Padfield PL, Altman D, et al. The British Hypertension Society Protocol for the evaluation of blood pressure measuring devices. J Hypertens. 1993;11(Suppl 2):S43–S63. - PubMed
-
- American National Standard for Electronic or Automated Sphygmomanometers: ANSI/AAMI SP10-1987. Arlington, VA: Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation; 1993. ; p40.
-
- The British Hypertension Society. Blood pressure measurement CD ROM. London: BMJ Books; 1998.
-
- Fagard R, Staessen J, Thijs L. Optimal definition of daytime and night-time blood pressure. Blood Press Monitor. 1997;2:315–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
