Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions
- PMID: 11337480
- PMCID: PMC311071
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.176601
Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions
Abstract
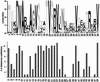
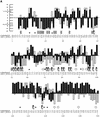
Many missense substitutions are identified in single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data and large-scale random mutagenesis projects. Each amino acid substitution potentially affects protein function. We have constructed a tool that uses sequence homology to predict whether a substitution affects protein function. SIFT, which sorts intolerant from tolerant substitutions, classifies substitutions as tolerated or deleterious. A higher proportion of substitutions predicted to be deleterious by SIFT gives an affected phenotype than substitutions predicted to be deleterious by substitution scoring matrices in three test cases. Using SIFT before mutagenesis studies could reduce the number of functional assays required and yield a higher proportion of affected phenotypes. may be used to identify plausible disease candidates among the SNPs that cause missense substitutions.
Figures



References
-
- Bell C, Lewis M. A closer view of the conformation of the Lac repressor bound to operator. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:209–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
