Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 mediates growth suppressive and apoptotic effects of interferon-beta in ovarian carcinoma cells
- PMID: 11337497
- PMCID: PMC2025680
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M101161200
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 mediates growth suppressive and apoptotic effects of interferon-beta in ovarian carcinoma cells
Abstract
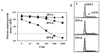
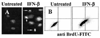
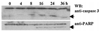
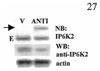
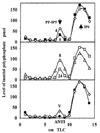
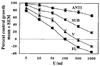
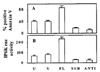
Interferons (IFNs) regulate the expression of genes that mediate their antiviral, antitumor, and immunomodulatory actions. We have previously shown that IFN-beta suppresses growth of human ovarian carcinoma xenografts in vivo and induces apoptosis of ovarian carcinoma cells in vitro. To investigate mechanisms of IFN-beta-induced apoptosis we employed an antisense technical knockout approach to identify gene products that mediate cell death and have isolated several regulators of interferon-induced death (RIDs). In this investigation, we have characterized one of the RIDs, RID-2. Sequence analysis revealed that RID-2 was identical to human inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (IP6K2). IP6K2 is post-transcriptionally induced by IFN-beta in ovarian carcinoma cells. A mutant IP6K2 with substitutions in the putative inositol phosphate binding domain abrogates IFN-beta-induced apoptosis. These studies identify a novel function for IP6K2 in cell growth regulation and apoptosis.
Figures




References
-
- Evinger M, Rubinstein M, Pestka S. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1981;210:319–329. - PubMed
-
- Kalvakolanu DV. Histol. Histopathol. 2000;15:523–537. - PubMed
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JEJ. Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

