Modeling advection and diffusion of oxygen in complex vascular networks
- PMID: 11339327
- PMCID: PMC3915047
- DOI: 10.1114/1.1359450
Modeling advection and diffusion of oxygen in complex vascular networks
Abstract
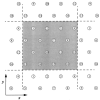
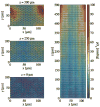
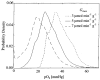
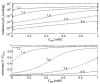
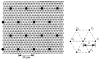
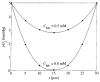
A realistic geometric model for the three-dimensional capillary network geometry is used as a framework for studying the transport and consumption of oxygen in cardiac tissue. The nontree-like capillary network conforms to the available morphometric statistics and is supplied by a single arterial source and drains into a pair of venular sinks. We explore steady-state oxygen transport and consumption in the tissue using a mathematical model which accounts for advection in the vascular network, nonlinear binding of dissolved oxygen to hemoglobin and myoglobin, passive diffusion of freely dissolved and protein-bound oxygen, and Michaelis-Menten consumption in the parenchymal tissue. The advection velocity field is found by solving the hemodynamic problem for flow throughout the network. The resulting system is described by a set of coupled nonlinear elliptic equations, which are solved using a finite-difference numerical approximation. We find that coupled advection and diffusion in the three-dimensional system enhance the dispersion of oxygen in the tissue compared to the predictions of simplified axially distributed models, and that no "lethal corner," or oxygen-deprived region occurs for physiologically reasonable values for flow and consumption. Concentrations of 0.5-1.0 mM myoglobin facilitate the transport of oxygen and thereby protect the tissue from hypoxia at levels near its P50, that is, when local oxygen consumption rates are close to those of delivery by flow and myoglobin-facilitated diffusion, a fairly narrow range.
Figures




References
-
- Batra S, Rakusan K. Morphometric analysis of capillary nets in rat myocardium. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;277:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Beard DA. Computational framework for generating transport models from databases of microvascular anatomy. Ann Biomed Eng. 2001;29(10):837–843. - PubMed
-
- Bentley TB, Meng H, Pittman RN. Temperature dependence of oxygen diffusion and consumption in mammalian striated muscle. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:H1825–H1830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
