Age-related differences in in-hospital mortality and the use of thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 11341137
- PMCID: PMC81018
Age-related differences in in-hospital mortality and the use of thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Recent guidelines have acknowledged that thrombolysis decreases mortality from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) independently of age. The purpose of this study was to determine the age-related rates of thrombolytic administration and in-hospital mortality and the variables related to the use of thrombolytic therapy for patients with AMI.
Methods: A prospective cohort analysis involved a registry of 44 acute care Quebec hospitals that enrolled 3741 patients with AMI between January 1995 and May 1996. The main outcomes of interest were crude and adjusted age-related in-hospital mortality rates and rates of use of thrombolytic therapy.
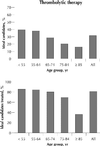
Results: In-hospital mortality rates increased dramatically with age from 2.1% in patients with AMI who were less than 55 years of age to 26.3% in those who were 85 years of age or older. Overall, 35.8% of the patients received thrombolysis. There was a pronounced inverse gradient in the use of thrombolysis with age, ranging from 46.2% in the youngest age group (< 55 years) to 9.5% in the oldest group (> or = 85 years). After adjustment for potential confounders, the older patients remained significantly less likely to receive thrombolytic therapy. Compared with patients who were less than 55 years of age, the odds ratio of receiving thrombolytic therapy was 0.68 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.52-0.89) for patients aged 65-74 years, 0.48 (95% CI 0.35-0.65) for patients aged 75-84 years and 0.13 (95% CI 0.06-0.26) for patients aged 85 years or more. Other variables related to thrombolytic therapy were diabetes (odds ratio [OR] 0.77, 95% CI 0.59-1.00), cerebrovascular disease (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.30-0.72), angina (OR 0.73, 95% CI 0.56-0.95), typical chest pain (OR 2.56, 95% CI 1.88-3.47); ST elevation (OR 8.93, 95% CI 7.24-11.00), Q wave MI (OR 5.26, 95% CI 4.20-6.60) and increased length of time between onset of symptoms and arrival at hospital.
Interpretation: Age is an important independent predictor of in-hospital mortality and lower thrombolytic use following AMI. Other studies are required to further evaluate the appropriateness of thrombolytic therapy for elderly patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Thrombolytics in elderly patients: a triumph of hope over experience?CMAJ. 2001 May 1;164(9):1301-3. CMAJ. 2001. PMID: 11341140 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The delay to thrombolysis: an analysis of hospital and patient characteristics. Quebec Acute Coronary Care Working Group.CMAJ. 1998 Feb 24;158(4):475-80. CMAJ. 1998. PMID: 9627559 Free PMC article.
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction assessment among patients with acute myocardial infarction and its association with hospital quality of care and evidence-based therapy use.Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012 Sep 1;5(5):662-71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.112.965012. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012. PMID: 22949495
-
Age-related trends (1986-1993) in the use of thrombolytic agents in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The Worcester Heart Attack Study.Arch Intern Med. 1997 Apr 14;157(7):741-6. Arch Intern Med. 1997. PMID: 9125005
-
[Clinical characteristics and hospital mortality of acute myocardial infarction in elderly patients treated with thrombolytic agents].Rev Esp Cardiol. 1996 Jul;49(7):501-8. Rev Esp Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8754444 Review. Spanish.
-
Thrombolytics in elderly patients: a triumph of hope over experience?CMAJ. 2001 May 1;164(9):1301-3. CMAJ. 2001. PMID: 11341140 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Association of Low Expression of NUMB in Peripheral Blood with Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cardiol Res Pract. 2022 Apr 26;2022:7981637. doi: 10.1155/2022/7981637. eCollection 2022. Cardiol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35529060 Free PMC article.
-
Is Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Counterpulsation Sufficient to Treat Patients in Cardiogenic Shock, Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Cardiol Res. 2015 Dec;6(6):339-345. doi: 10.14740/cr415w. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Cardiol Res. 2015. PMID: 28197255 Free PMC article.
-
ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction in the elderly.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2012 Jun;9(2):108-14. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1263.2011.12297. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22916055 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in a provision of in-hospital post-arrest interventions for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) in the elderly population-protocol for a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 7;5:55. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0234-4. Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27142791 Free PMC article.
-
Use of thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: effects of gender and age on treatment rates.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2002 Feb;13(1):21-6. doi: 10.1023/a:1015312007648. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2002. PMID: 11994556
References
-
- Udvarhelyi IS, Gatsonis C, Epstein AM, Pashos CL, Newhouse JP, McNeil BJ. Acute myocardial infarction in the Medicare population. Process of care and clinical outcomes. JAMA 1992;268(18):2530-6. - PubMed
-
- Maggioni AP, Maseri A, Fresco C, Franzosi MG, Mauri F, Santoro E, et al. Age-related increase in mortality among patients with first myocardial infarctions treated with thrombolysis. The Investigators of the Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell'Infarto Miocardico (GISSI-2). N Engl J Med 1993;329:1442-8. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Goldberg RJ, Chen Z, Gore JM, Alpert JS. Recent trends in hospital mortality of acute myocardial infarction — the Worcester Heart Attack Study. Have improvements been realized for all age groups? Arch Intern Med 1994;154:2202-8. - PubMed
-
- Randomized trial of intravenous streptokinase, oral aspirin, both, or neither among 17,187 cases of suspected acute myocardial infarction: ISIS-2. ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival) Collaborative Group. Lancet 1988;ii:349-60. - PubMed
-
- GISSI-2: a factorial randomised trial of alteplase versus streptokinase and heparin versus no heparin among 12,490 patients with acute myocardial infarction. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell'Infarto Miocardico. Lancet 1990;336:65-71 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
