Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is a novel inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases with implications for atherosclerosis
- PMID: 11342575
- PMCID: PMC209273
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10403
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 is a novel inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases with implications for atherosclerosis
Abstract
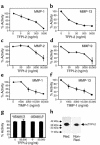
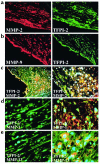
Degradation of ECM, particularly interstitial collagen, promotes plaque instability, rendering atheroma prone to rupture. Previous studies implicated matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in these processes, suggesting that dysregulated MMP activity, probably due to imbalance with endogenous inhibitors, promotes complications of atherosclerosis. We report here that the serine proteinase inhibitor tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) can function as an MMP inhibitor. TFPI-2 diminished the ability of the interstitial collagenases MMP-1 and MMP-13 to degrade triple-helical collagen, the primary load-bearing molecule of the ECM within human atheroma. In addition, TFPI-2 also reduced the activity of the gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. In contrast to the "classical" tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs), TFPI-2 expression in situ correlated inversely with MMP levels in human atheroma. TFPI-2 colocalized primarily with smooth muscle cells in the normal media as well as the plaque's fibrous cap. Conversely, the macrophage-enriched shoulder region, the prototypical site of matrix degradation and plaque rupture, stained only weakly for TFPI-2 but intensely for gelatinases and interstitial collagenases. Evidently, human mononuclear phagocytes, an abundant source of MMPs within human atheroma, lost their ability to express this inhibitor during differentiation in vitro. These findings establish a new, anti-inflammatory function of TFPI-2 of potential pathophysiological significance for human diseases, including atherosclerosis.
Figures




References
-
- Petersen LC, et al. Inhibitory properties of a novel human Kunitz-type protease inhibitor homologous to tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1996;35:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Butzow R, Huhtala ML, Bohn H, Virtanen I, Seppala M. Purification and characterization of placental protein 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;150:483–490. - PubMed
-
- Iino M, Foster DC, Kisiel W. Quantification and characterization of human endothelial cell-derived tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18:40–46. - PubMed
-
- Rao CN, Mohanam S, Puppala A, Rao JS. Regulation of ProMMP-1 and ProMMP-3 activation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2/matrix-associated serine protease inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;255:94–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

