Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 controls chemokine production and T helper cell type 2 cell trafficking in allergic pulmonary inflammation
- PMID: 11342593
- PMCID: PMC2193434
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.9.1087
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 controls chemokine production and T helper cell type 2 cell trafficking in allergic pulmonary inflammation
Abstract
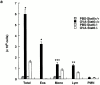
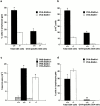
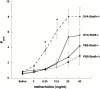
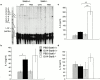
Antigen-specific CD4 T helper type 2 (Th2) cells play a pivotal role in the induction of allergic asthma, but the mechanisms regulating their recruitment into the airways are unknown. Signal transducer and activator of transcription factor (Stat)6 is a transcription factor essential for Th2 cell differentiation. Here we show that Stat6 also controls Th2 cell recruitment and effector function in allergic inflammation in vivo. To isolate the role of Stat6 in regulating Th2 cell trafficking and effector function from its role in Th2 cell differentiation, we used a murine model of asthma in which in vitro-differentiated Stat6(+/+) antigen-specific Th2 cells were adoptively transferred into naive Stat6(-/-) and Stat6(+/+) mice followed by aerosol antigen challenge. We found that all of the features of asthma, including Th2 cell accumulation, Th2 and eosinophil-active chemokine production, and airway eosinophilia, mucus production, and hyperresponsiveness seen in Stat6(+/+) mice, were dramatically absent in Stat6(-/)- mice that received Stat6(+/)+ antigen-specific Th2 cells. Our findings establish Stat6 as essential for Th2 cell trafficking and effector function and suggest that interruption of Stat6 signaling in resident cells of the lung is a novel approach to asthma therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
STAT6-mediated signaling in Th2-dependent allergic asthma: critical role for the development of eosinophilia, airway hyper-responsiveness and mucus hypersecretion, distinct from its role in Th2 differentiation.Int Immunol. 2004 Oct;16(10):1497-505. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh151. Epub 2004 Sep 6. Int Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15351784
-
Transfer of in vivo primed transgenic T cells supports allergic lung inflammation and FIZZ1 and Ym1 production in an IL-4Rα and STAT6 dependent manner.BMC Immunol. 2011 Oct 20;12:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-60. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22014099 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation of T helper type 2 cytokine-dependent airway lesions from signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 signalling in experimental chronic asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2003 May;33(5):688-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01647.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003. PMID: 12752600
-
STAT4 and STAT6, their role in cellular and humoral immunity and in diverse human diseases.Int Rev Immunol. 2024;43(6):394-418. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2024.2395274. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Int Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188021 Review.
-
Eosinophils and allergic airway disease: there is more to the story.Trends Immunol. 2010 Jan;31(1):39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.10.001. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Trends Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19926338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of targeted disruption of STAT4 and STAT6 on the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Clin Invest. 2001 Sep;108(5):739-47. doi: 10.1172/JCI12563. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11544280 Free PMC article.
-
Key mediators in the immunopathogenesis of allergic asthma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Nov;23(1):316-29. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.034. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24933589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tale of two STAT6 knock out mice in the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroimmunol. 2009 Jan 3;206(1-2):76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.11.003. Epub 2008 Dec 18. J Neuroimmunol. 2009. PMID: 19100630 Free PMC article.
-
STAT6 expression in multiple cell types mediates the cooperative development of allergic airway disease.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2571-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002567. Epub 2011 Jan 17. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21242523 Free PMC article.
-
Are mouse models of asthma appropriate for investigating the pathogenesis of airway hyper-responsiveness?Front Physiol. 2012 Jul 31;3:312. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00312. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23060800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wills-Karp M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Del Prete G.F., De Carli M., D'Elios M.M., Maestrelli P., Ricci M., Fabbri L., Romagnani S. Allergen exposure induces the activation of allergen-specific Th2 cells in the airway mucosa of patients with allergic respiratory disorders. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993;23:1445–1449. - PubMed
-
- Robinson D.S., Hamid Q., Ying S., Tsicopoulos A., Barkans J., Bentley A.M., Corrigan C., Durham S.R., Kay A.B. Predominant Th2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N. Eng. J. Med. 1992;326:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Walker C., Bode E., Boer L., Hansel T., Blaser K., Virchow C., Jr. Allergic and nonallergic asthmatics have distinct patterns of T-cell activation and cytokine production in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992;146:109–115. - PubMed
-
- Bruselle G.J., Kips G., Bluethmann G., Pauwels R. Allergen-induced airway inflammation and bronchial responsiveness in wildtype and IL-4 deficient mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Biol. 1995;12:254–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

