Immunocytochemical evidence for co-expression of Type III IP3 receptor with signaling components of bitter taste transduction
- PMID: 11346454
- PMCID: PMC31433
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-6
Immunocytochemical evidence for co-expression of Type III IP3 receptor with signaling components of bitter taste transduction
Abstract
Background: Taste receptor cells are responsible for transducing chemical stimuli into electrical signals that lead to the sense of taste. An important second messenger in taste transduction is IP3, which is involved in both bitter and sweet transduction pathways. Several components of the bitter transduction pathway have been identified, including the T2R/TRB taste receptors, phospholipase C beta2, and the G protein subunits alpha-gustducin, beta3, and gamma13. However, the identity of the IP3 receptor subtype in this pathway is not known. In the present study we used immunocytochemistry on rodent taste tissue to identify the IP3 receptors expressed in taste cells and to examine taste bud expression patterns for IP3R3.
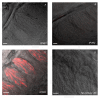
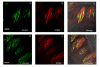
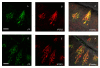
Results: Antibodies against Type I, II, and III IP3 receptors were tested on sections of rat and mouse circumvallate papillae. Robust cytoplasmic labeling for the Type III IP3 receptor (IP3R3) was found in a large subset of taste cells in both species. In contrast, little or no immunoreactivity was seen with antibodies against the Type I or Type II IP3 receptors. To investigate the potential role of IP3R3 in bitter taste transduction, we used double-label immunocytochemistry to determine whether IP3R3 is expressed in the same subset of cells expressing other bitter signaling components. IP3R3 immunoreactive taste cells were also immunoreactive for PLCbeta2 and gamma13. Alpha-gustducin immunoreactivity was present in a subset of IP3R3, PLCbeta2, and gamma13 positive cells.
Conclusions: IP3R3 is the dominant form of the IP3 receptor expressed in taste cells and our data suggest it plays an important role in bitter taste transduction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of gustducin overlaps with that of type III IP3 receptor in taste buds of the rat soft palate.Chem Senses. 2007 Sep;32(7):689-96. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjm036. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Chem Senses. 2007. PMID: 17566068
-
IP(3) receptor type 3 and PLCbeta2 are co-expressed with taste receptors T1R and T2R in rat taste bud cells.Chem Senses. 2001 Mar;26(3):259-65. doi: 10.1093/chemse/26.3.259. Chem Senses. 2001. PMID: 11287386
-
Lrmp/Jaw1 is expressed in sweet, bitter, and umami receptor-expressing cells.Chem Senses. 2010 Feb;35(2):171-7. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjp097. Chem Senses. 2010. PMID: 20071408 Free PMC article.
-
Taste receptor signalling - from tongues to lungs.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Feb;204(2):158-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02308.x. Epub 2011 May 7. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21481196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sweet and the bitter of mammalian taste.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004 Aug;14(4):423-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.06.003. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15321062 Review.
Cited by
-
Honing in on the ATP Release Channel in Taste Cells.Chem Senses. 2015 Sep;40(7):449-51. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv035. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Chem Senses. 2015. PMID: 26126730 Free PMC article.
-
Ric-8A, a Galpha protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor potentiates taste receptor signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2009 Oct 8;3:11. doi: 10.3389/neuro.03.011.2009. eCollection 2009. Front Cell Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19847316 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of different taste buds and expression of alpha-gustducin in the barbells of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2006 Mar;32(1):55-62. doi: 10.1007/s10695-006-6937-z. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2006. PMID: 20035479
-
Qualitative and quantitative differences between taste buds of the rat and mouse.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Jan 5;8:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-5. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17207280 Free PMC article.
-
A succinate/SUCNR1-brush cell defense program in the tracheal epithelium.Sci Adv. 2023 Aug 2;9(31):eadg8842. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg8842. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37531421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindemann B. Taste reception. Physiol Rev. 1996;76:718–766. - PubMed
-
- Glendinning JI, Chaudhari N, Kinnamon SC. Taste transduction and molecular biology. The Neurobiology of Taste and Smell (Edited by Finger TE, Silver WL, Restrepo D,) 2nd ed. New York: Wiley-Liss; 2000. pp. 315–351.
-
- Akabas MH, Dodd J, Al-Awqati Q. A bitter substance induces a rise in intracellular calcium in a subpopulation of rat taste cells. Science. 1988;242:1047–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

