Tumor necrosis factor-dependent adhesions as a major protective mechanism early in septic peritonitis in mice
- PMID: 11349012
- PMCID: PMC98332
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.3550-3555.2001
Tumor necrosis factor-dependent adhesions as a major protective mechanism early in septic peritonitis in mice
Abstract
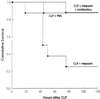
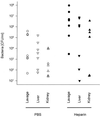
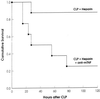
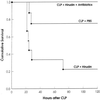
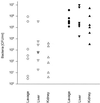
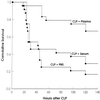
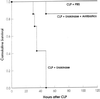
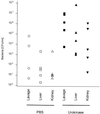
The occurrence of peritoneal adhesions in surgical patients is positively correlated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) levels. In a model of septic peritonitis-cecal ligation and puncture-TNF neutralization prevented formation of peritoneal adhesions and increased mortality, most likely because localization of the septic focus was prevented. To discriminate between the coagulation-independent protective TNF effect and a potential protective procoagulant TNF effect, formation of peritoneal adhesions after CLP was inhibited with heparin, hirudin, or urokinase. Each treatment increased mortality and increased the number of bacteria in the peritoneal lavage fluid, kidney, and liver to various degrees. Under these experimental conditions, antibiotics prevented death. In coagulation-compromised mice, lethality was further enhanced by additional TNF neutralization. These findings demonstrate that peritoneal adhesions early in septic peritonitis are an important mechanism of innate immunity that prevents increased spread of bacteria and reduces mortality.
Figures
References
-
- Bagby G J, Plessala K J, Wilson L A, Thompson J J, Nelson S. Divergent efficacy of antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in intravascular and peritonitis models of sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1991;163:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Billing A G, Fröhlich D, Konecny G, Schildberg F W, Machleidt W, Fritz H, Jochum M. Local serum application: restoration of sufficient host defense in human peritonitis. Eur J Clin Investig. 1994;24:28–35. - PubMed
-
- Bone R C. Modulators of coagulation. A critical appraisal of their role in sepsis. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152:1381–1389. - PubMed
-
- Dickneite G, Czech J. Combination of antibiotic treatment with the thrombin inhibitor recombinant hirudin for the therapy of experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 1994;71:768–772. - PubMed
-
- Dickneite G, Czech J, Keuper H. Formation of fibrin monomers in experimental disseminated intravascular coagulation and its inhibition by recombinant hirudin. Circ Shock. 1994;42:183–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

