Early local cytokine profiles in strains of mice with different outcomes from chlamydial genital tract infection
- PMID: 11349013
- PMCID: PMC98334
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.3556-3561.2001
Early local cytokine profiles in strains of mice with different outcomes from chlamydial genital tract infection
Abstract
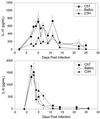
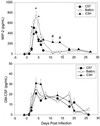
In this study, we expand on the examination of genetically determined differences in host responses that correlate with clearance of Chlamydia trachomatis from the genital tract. We infected C57BL/6, BALB/c, and C3H/HeN mice with the mouse pneumonitis agent of C. trachomatis (MoPn). C57BL/6 mice had the shortest course of infection (22 days) and the lowest incidence of severe hydrosalpinx. BALB/c mice also had a short course of infection (25 days), but all developed hydrosalpinx. C3H/HeN mice had the longest course of infection (38 days), and all developed severe hydrosalpinx. Determination of local cytokine responses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of genital tract secretions revealed that the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) were significantly increased in the C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains compared to those in the C3H/HeN strain whereas the level of IL-6 was not different. The level of the neutrophil chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2) was increased during the first week of infection in all three strains but was significantly higher in the BALB/c strain, the strain with the most rapid influx of neutrophils into the genital tract. Prolonged detection of MIP-2 in C3H/HeN mice was associated with a protracted presence of neutrophils in the genital tract. Early increases in the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1beta are associated with earlier eradication of infection in the C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains than in the C3H/HeN strain. Increased levels of MIP-2 and neutrophils in BALB/c and C3H/HeN mice relative to C57BL/6 mice suggest that these responses may contribute to pathology.
Figures
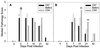
References
-
- Appelberg R. Macrophage inflammatory proteins MIP-1 and MIP-2 are involved in T cell-mediated neutrophil recruitment. J Leukoc Biol. 1992;52:303–306. - PubMed
-
- Cacalano G, Lee J, Kikly K, Ryan A M, Pitts-Meek S, Hultgren B, Wood W I, Moore M W. Neutrophil and B cell expansion in mice that lack the murine IL-8 receptor homolog. Science. 1994;265:682–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

