Differential interleukin-10 and gamma interferon mRNA expression in lungs of cilium-associated respiratory bacillus-infected mice
- PMID: 11349033
- PMCID: PMC98372
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.3697-3702.2001
Differential interleukin-10 and gamma interferon mRNA expression in lungs of cilium-associated respiratory bacillus-infected mice
Abstract
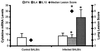
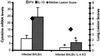
The cilium-associated respiratory (CAR) bacillus is a gram-negative, extracellular bacterium that causes persistent respiratory tract infections in rodents. We have previously demonstrated that BALB/c mice are more susceptible to CAR bacillus-induced disease than resistant C57BL/6 mice, with elevations in pulmonary gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin (IL)-4. IL-10 is a type 2 cytokine that can increase host susceptibility to bacterial diseases through its anti-inflammatory effects, including suppression of macrophage function. The purpose of this study was to further describe the cytokine profiles associated with histologic lesions in CAR bacillus-infected mice and to assess the effects of cytokine depletion on the pathogenesis of disease. Six-week-old female BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice and mice with targeted mutations in IFN-gamma and IL-4 were inoculated intratracheally with 10(5) CAR bacillus organisms, and samples were collected at 6 to 7 weeks postinoculation. Lung samples were collected for histopathologic examination and analysis of cytokine mRNA. IFN-gamma, IL-10, and IL-4 mRNA levels in the lungs of infected mice were semiquantitatively measured using a reverse transcriptase-mediated PCR assay and compared to those in uninfected control animals of each strain. BALB/c mice infected with CAR bacillus had a median lung lesion score of 6 and IL-10 and IL-4 mRNA levels were significantly elevated. The majority of C57BL/6 mice were resistant to disease characterized by lung lesions scores of 2 or less and a dominant IFN-gamma mRNA cytokine profile. A few C57BL/6 mice with lesions scores of 5 or greater had elevations in all three cytokines and were susceptible to disease. C57BL/6 IFN-gamma knockout mice had increased disease with elevations in IL-10 and IL-4 mRNA, while BALB/c IL-4 knockout mice infected with CAR bacillus had a mild decrease in lesion severity and an attenuated IL-10 mRNA expression compared to wild-type BALB/c mice. These data indicate that IL-10 and IL-4 predominate in CAR bacillus-induced histologic lesions in mice, while IFN-gamma may play a role in resistance to disease.
Figures
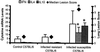

References
-
- Brogden K A, Cutlip R C, Lehmkuhl H D. Cilia-associated respiratory bacillus in wild rats in central Iowa. J Wildlife Dis. 1993;29:123–126. - PubMed
-
- DeMaeyer E, Demaeyer-Guignard J. Interferons. In: Thomson A W, editor. The cytokine handbook. 2nd ed. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1994. p. 265-288.
-
- Faulkner C B, Simecka J W, Davidson M K, Davis J K, Schoeb T R, Lindsey J R, Everson M P. Gene expression and production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, interleukin 6, and gamma interferon in C3H/HeN and C57BL/6N mice in acute Mycoplasma pulmonis disease. Infect Immun. 1995;63:4084–4090. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fiorentino D F, Zlotnik A, Mosmann T R, Howard M, O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991;147:3815–3822. - PubMed
-
- Fitch F W, McKisic M D, Lancki D W, Gajewski T F. Differential regulation of murine T lymphocyte subsets. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:29–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

