Ureaplasma urealyticum modulates endotoxin-induced cytokine release by human monocytes derived from preterm and term newborns and adults
- PMID: 11349058
- PMCID: PMC98421
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.3906-3915.2001
Ureaplasma urealyticum modulates endotoxin-induced cytokine release by human monocytes derived from preterm and term newborns and adults
Abstract
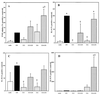
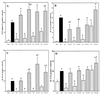
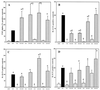
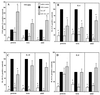
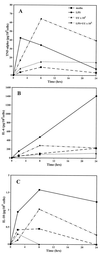
We previously observed that Ureaplasma urealyticum respiratory tract colonization in infants with a birth weight of < or =1,250 g was associated with increases in the tracheal aspirate proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) relative to the counterregulatory cytokine IL-6 during the first week of life (A. M. Patterson, V. Taciak, J. Lovchik, R. E. Fox, A. B. Campbell, and R. M. Viscardi, Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 17:321-328, 1998). We hypothesized that U. urealyticum alters the host immune response in the presence of a coinflammatory stimulus (e.g., bacterial infection or hyperoxia) by shifting the balance of cytokine expression towards the proinflammatory cytokines. To test this hypothesis, we compared the release of TNF-alpha, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-10 in vitro by unstimulated and U. urealyticum (with or without lipopolysaccharide [LPS])-stimulated human monocytes from adult peripheral blood and from term and preterm cord blood. U. urealyticum alone and in combination with LPS induced concentration- and development-dependent changes in cytokine release. In vitro inoculation with low-inoculum U. urealyticum (10(3) color-changing units [CCU]) (i) partially blocked the LPS-stimulated IL-6 release by all cells and reduced LPS-stimulated IL-10 release by preterm cells, (ii) stimulated TNF-alpha and IL-8 release by preterm cells, and (iii) augmented LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha release in all cells. In preterm cells, high-inoculum U. urealyticum (10(6) CCU) (i) stimulated TNF-alpha and IL-8, but not IL-6 or IL-10, release and (ii) augmented LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha and IL-8 release. High-inoculum U. urealyticum (i) stimulated release of all four cytokines in term cells and IL-8 release in adult cells and (ii) augmented LPS-induced TNF-alpha, IL-10, and IL-8 release in term cells but did not significantly affect LPS-induced cytokine release in adult cells. We speculate that U. urealyticum enhances the proinflammatory response to a second infection by blocking expression of counterregulatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-10), predisposing the preterm infant to prolonged and dysregulated inflammation, lung injury, and impaired clearance of secondary infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ureaplasma Species Differentially Modulate Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Responses in Newborn and Adult Human Monocytes Pushing the State Toward Pro-Inflammation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 28;7:484. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00484. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29234642 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of progesterone on proinflammatory cytokine production by monocytes stimulated with pathogens associated with preterm birth.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008 Oct;60(4):346-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2008.00633.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19046141
-
Ureaplasma urealyticum-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines by macrophages.Pediatr Res. 2000 Jul;48(1):114-9. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200007000-00020. Pediatr Res. 2000. PMID: 10879809
-
Leukocyte counts and colonization with Ureaplasma urealyticum in preterm neonates.Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17 Suppl 1:S144-7. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.supplement_1.s144. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. PMID: 8399905 Review.
-
Role of erythromycin for treatment of incipient chronic lung disease in preterm infants colonised with Ureaplasma urealyticum.Drugs. 2001;61(13):1893-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161130-00002. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11708762 Review.
Cited by
-
The Maternal Serological Response to Intrauterine Ureaplasma sp. Infection and Prediction of Risk of Pre-Term Birth.Front Immunol. 2014 Dec 9;5:624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00624. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25538708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal Ureaplasma Exposure Is Associated With Increased Risk of Late Onset Sepsis and Imbalanced Inflammation in Preterm Infants and May Add to Lung Injury.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 2;9:68. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00068. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31001484 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Vaginal Ureaplasma spp. Colonization in Early Pregnancy Is Associated with Adverse Short- and Long-Term Outcome of Very Preterm Infants.Children (Basel). 2021 Apr 3;8(4):276. doi: 10.3390/children8040276. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916723 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between pathogenic bacteria and intrauterine leukocytes triggers alternative molecular signaling cascades leading to labor in women.Infect Immun. 2010 Nov;78(11):4792-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00522-10. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20805331 Free PMC article.
-
Ureaplasma Species Differentially Modulate Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Responses in Newborn and Adult Human Monocytes Pushing the State Toward Pro-Inflammation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 28;7:484. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00484. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29234642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abele-Horn M, Genzel-Boroviczeny O, Uhlig T, Zimmermann A, Peteres J, Scholz M. Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a comparative prospective muticentre study. Eur J Pediatr. 1998;157:1004–1011. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi A, Viscardi R M, Taciak V, Ensor J E, McCrea K A, Hasday J D. Increased activity of interleukin-6 but not tumor necrosis factor-α in lung lavage of premature infants is associated with the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res. 1994;36:244–252. - PubMed
-
- Boyum A. Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow with special reference to factors which influence and modify sedimentation properties of hematopoietic cells. Scand J Clin Investig. 1968;21(Suppl.):1–109.
-
- Cheda S, Palkowetz K H, Garofalo R, Rassin D K, Goldman A S. Decreased interleukin-10 production by neonatal monocytes and T cells: relationship to decreased production and expression of tumor necrosis factor-α and its receptors. Pediatr Res. 1996;40:475–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

