Anaerobic conditions induce expression of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 11349079
- PMCID: PMC98472
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.4079-4085.2001
Anaerobic conditions induce expression of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
Products of the intercellular adhesion (ica) operon in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis synthesize a linear beta-1,6-linked glucosaminylglycan. This extracellular polysaccharide mediates bacterial cell-cell adhesion and is required for biofilm formation, which is thought to increase the virulence of both pathogens in association with prosthetic biomedical implants. The environmental signal(s) that triggers ica gene product and polysaccharide expression is unknown. Here we demonstrate that anaerobic in vitro growth conditions lead to increased polysaccharide expression in both S. aureus and S. epidermidis, although the regulation is less stringent in S. epidermidis. Anaerobiosis also dramatically stimulates ica-specific mRNA expression in ica- and polysaccharide-positive strains of both S. aureus and S. epidermidis. These data suggest a mechanism whereby ica gene expression and polysaccharide production may act as a virulence factor in an anaerobic environment in vivo.
Figures


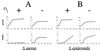
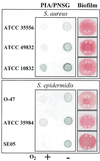

References
-
- Arvidson S. Extracellular enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. In: Easmon C S F, Adlam C, editors. Staphylococci and staphylococcal infections. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press; 1983. pp. 745–808.
-
- Brückner R. Gene replacement in Staphylococcus carnosus and Staphylococcus xylosus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;151:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Christensen G D, Bisno A L, Parisi J T, McLaughlin B, Ester M G H, Luther R W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982;96:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

