Influence of cultivation media on genetic regulatory patterns in Borrelia burgdorferi
- PMID: 11349092
- PMCID: PMC98485
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.4159-4163.2001
Influence of cultivation media on genetic regulatory patterns in Borrelia burgdorferi
Abstract
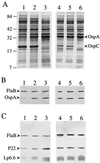
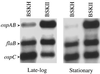
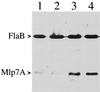
Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly II (BSKII) medium and BSKH medium both are routinely used for the cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi. However, heretofore there have been no studies to compare how these two media affect gene expression patterns in virulent B. burgdorferi. In the present study, we found that some B. burgdorferi strain 297 genes (e.g., ospA, mlp-7A, mlp-8, p22, and lp6.6) that typically are regulated by temperature or pH displayed their predicted pattern of expression when B. burgdorferi was cultivated in BSKH medium; this was not true when spirochetes were cultivated in conventional BSKII medium. The results suggest that BSKH medium is superior to BSKII medium for gene expression studies with B. burgdorferi.
Figures

References
-
- Akins D R, Porcella S F, Popova T G, Shevchenko D, Li M, Norgard M V, Radolf J D. Evidence for in vivo but not in vitro expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein F (OspF) homologue. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:507–520. - PubMed
-
- Alban P S, Johnson P W, Nelson D R. Serum-starvation-induced changes in protein synthesis and morphology of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiology. 2000;146:119–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

