Large-scale deletion and point mutations of the nuclear NDUFV1 and NDUFS1 genes in mitochondrial complex I deficiency
- PMID: 11349233
- PMCID: PMC1226121
- DOI: 10.1086/320603
Large-scale deletion and point mutations of the nuclear NDUFV1 and NDUFS1 genes in mitochondrial complex I deficiency
Abstract
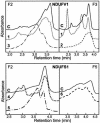
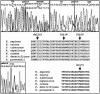
Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH):ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) is the largest complex of the mitochondrial respiratory chain and complex I deficiency accounts for approximately 30% cases of respiratory-chain deficiency in humans. Only seven mitochondrial DNA genes, but >35 nuclear genes encode complex I subunits. In an attempt to elucidate the molecular bases of complex I deficiency, we studied the six most-conserved complex I nuclear genes (NDUFV1, NDUFS8, NDUFS7, NDUFS1, NDUFA8, and NDUFB6) in a series of 36 patients with isolated complex I deficiency by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography and by direct sequencing of the corresponding cDNA from cultured skin fibroblasts. In 3/36 patients, we identified, for the first time, five point mutations (del222, D252G, M707V, R241W, and R557X) and one large-scale deletion in the NDUFS1 gene. In addition, we found six novel NDUFV1 mutations (Y204C, C206G, E214K, IVS 8+41, A432P, and del nt 989-990) in three other patients. The six unrelated patients presented with hypotonia, ataxia, psychomotor retardation, or Leigh syndrome. These results suggest that screening for complex I nuclear gene mutations is of particular interest in patients with complex I deficiency, even when normal respiratory-chain-enzyme activities in cultured fibroblasts are observed.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www2.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/query_form.html (for NDUFV1 [AF053070, AF053069], NDUFS1 [NM005006, AC007383], NDUFS8 [U65579], NDUFS7 [AC005329], NDUFA8 [NM014222], and NDUFB6 [NM002493])
-
- Généthon, http://www.genethon.fr
-
- MITOMAP Human mitochondrial genome database, http://www.gen.emory.edu/mitomap.html
References
-
- Allikmets R, Raskind WH, Hutchinson A, Schueck ND, Dean M, Koeller DM (1999) Mutation of a putative mitochondrial iron transporter gene (ABC7) in X-linked sideroblastic anemia and ataxia (XLSA/A). Hum Mol Genet 8:743–749 - PubMed
-
- Amiel J, Gigarel N, Benacki A, Bénit P, Valnot I, Parfait B, von Kleist-Retzow JC, Raclin V, Hadj-Rabia S, Dumez Y, Rustin P, Bonnefont JP, Munnich A, Rötig A. Prenatal diagnosis of respiratory chain deficiency by direct mutation screening. Prenatal Diagnosis (in press) - PubMed
-
- Campuzano V, Montermini L, Molto MD, Pianese L, Cossee M, Cavalcanti F, Monros E, Rodius F, Duclos F, Monticelli A, et al (1996) Friedreich's ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science 271:1423–1427 - PubMed
-
- Delettre C, Lenaers G, Griffoin JM, Gigarel N, Lorenzo C, Belenguer P, Pelloquin L, Grosgeorge J, Turc-Carel C, Perret E, Astarie-Dequeker C, Lasquellec L, Arnaud B, Ducommun B, Kaplan J, Hamel CP (2000) Nuclear gene OPA1, encoding a mitochondrial dynamin-related protein, is mutated in dominant optic atrophy. Nat Genet 26:207–210 - PubMed
-
- Dib C, Faure S, Fizames C, Samson D, Drouot N, Vignal A, Millasseau P, Marc S, Hazan J, Seboun E, Lathrop M, Gyapay G, Morissette J, Weissenbach J (1996) A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature 380:152–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

