Differential prevention of morphine amnesia by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides directed against various Gi-protein alpha subunits
- PMID: 11350863
- PMCID: PMC1572787
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704081
Differential prevention of morphine amnesia by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides directed against various Gi-protein alpha subunits
Abstract
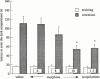
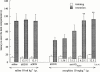
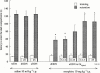
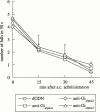
The effect of the i.c.v. administration of pertussis toxin (PTX) and antisense oligodeoxynucleotide directed against the alpha subunit of different Gi-proteins (anti-Gialpha1, anti-Gialpha2, anti-Gialpha3) on amnesia induced by morphine was evaluated in the mouse passive avoidance test. The administration of morphine (6 - 10 mg kg(-1) i.p.) immediately after the training session produced amnesia that was prevented by PTX (0.25 microg per mouse i.c.v.) administered 7 days before the passive avoidance test. Anti-Gialpha1 (6.25 microg per mouse i.c.v.) and anti-Gialpha3 (12.5 microg per mouse i.c.v.), administered 18 and 24 h before the training session, prevented the morphine amnesia. By contrast, pretreatment with anti-Gialpha2 (3.12 - 25 microg per mouse i.c.v.) never modified the impairment of memory processes induced by morphine. At the highest effective doses, none of the compounds used impaired motor coordination, as revealed by the rota rod test, nor modified spontaneous motility and inspection activity, as revealed by the hole board test. These results suggest the important role played by Gi1 and Gi3 protein subtypes in the transduction mechanism involved in the impairment of memory processes produced by morphine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alpha-2 agonists induce amnesia through activation of the Gi-protein signalling pathway.Neuroscience. 2004;126(2):451-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.04.001. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15207363
-
Role of Gi proteins in the antidepressant-like effect of amitriptyline and clomipramine.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002 Oct;27(4):554-64. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00340-8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12377392
-
Diphenhydramine-induced amnesia is mediated by Gi-protein activation.Neuroscience. 2003;122(2):471-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.005. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 14614911
-
Inactivation of Gi proteins induces an antidepressant-like effect in the mouse forced-swimming test.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Sep;43(3):457-65. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00089-8. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12243776
-
Neuroendocrine and behavioral effects of antisense oligonucleotides.Eur J Endocrinol. 1997 Oct;137(4):326-35. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1370326. Eur J Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9368496 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Proteome Analysis of Rat Hippocampus Following Morphine-induced Amnesia and State-dependent Learning.Iran J Pharm Res. 2015 Spring;14(2):591-602. Iran J Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25901168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BURFORD N.T., TOLBERT L.M., SADEE W. Specific G protein activation and μ-opioid receptor internalization caused by morphine, DAMGO and endomorphin I. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998;342:123–126. - PubMed
-
- CAPACCIOLI S., DI PASQUALE G., MINI E., MAZZEI T., QUATTRONE A. Cationic lipids improve antisense oligonucleotide uptake and prevent degradation in cultured cells and in human serum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1993;107:818–825. - PubMed
-
- CASTELLANO C. Effects of morphine and heroin on discrimination, learning, and consolidation in mice. Psychopharmacologia. 1975;42:235–242. - PubMed
-
- CASTELLANO C., PAVONE F. Dose- and strain-dependent effects of dermorphin and [D-Ala2-D-Leu5]enkephalin on passive avoidance behavior in mice. Behav. Neurosci. 1985;99:1120–1127. - PubMed
-
- CHAKRABARTI S., PRATHER P.L., YU L., LAW P.Y., LOH H.H. Expression of the mu-opioid receptor in CHO cells: ability of mu-opioid ligands to promote alpha-azidoanilido[32P]GTP labeling of multiple G protein alpha subunits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995;64:2534–2543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

