Pharmacological aids to locomotor training after spinal injury in the cat
- PMID: 11351014
- PMCID: PMC2278596
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0065b.x
Pharmacological aids to locomotor training after spinal injury in the cat
Abstract
This Topical Review summarizes some of the work we have done mainly in the cat using agonists and antagonists of various neurotransmitter systems injected intravenously or intrathecally to initiate or modulate the expression of hindlimb locomotion after a spinal lesion at T13. The effects of the same drugs are compared in various preparations: complete spinal, partial spinal or intact cats. This has revealed that there can be major differences in these effects. In turn, this suggests that although the locomotor rhythm might normally be triggered and modulated by the activation of a variety of receptors (noradrenaline, serotonin, glutamate), after spinalization there appears to be a predominance of glutamatergic mechanisms. Recent work also suggests that, in the cat, the integrity of the midlumbar segments is crucial for the expression of spinal locomotion. Taken together, this work raises some hope that a targeted pharmacotherapy with better understood drugs and mode and locus of delivery could become a clinical reality.
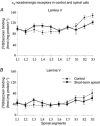
Figures



References
-
- Baev KV. Rhythmic discharges in hindlimb motor nerves of the decerebrate, immobolized cat induced by intravenous injection of DOPA. Neurophysiology. 1977;9:165–167. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau H, Chau C, Rossignol S. Noradrenergic agonists and locomotor training affect locomotor recovery after cord transection in adult cats. Brain Research Bulletin. 1993;30:387–393. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau H, Julien C, Rossignol S. The effects of clonidine and yohimbine on locomotion and cutaneous reflexes in the adult chronic spinal cat. Brain Research. 1987;437:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau H, Rossignol S. Recovery of locomotion after chronic spinalization in the adult cat. Brain Research. 1987;412:84–95. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau H, Rossignol S. The effects of serotonergic drugs on the locomotor pattern and on cutaneous reflexes of the adult chronic spinal cat. Brain Research. 1990;514:55–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

