Stretch-dependent potassium channels in murine colonic smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 11351024
- PMCID: PMC2278597
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0155b.x
Stretch-dependent potassium channels in murine colonic smooth muscle cells
Abstract
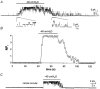
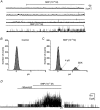
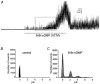
Gastrointestinal muscles are able to maintain negative resting membrane potentials in spite of stretch. We investigated whether stretch-dependent K+ channels might contribute to myogenic regulation of smooth muscle cells from the mouse colon. Negative pressure applied to on-cell membrane patches activated K+ channels that were voltage independent and had a slope conductance of 95 pS in symmetrical K+ gradients. The effects of negative pressure on open probability were graded as a function of pressure and reversible when atmospheric pressure was restored. Cell elongation activated K+ channels with the same properties as those activated by negative pressure, suggesting that the channels were stretch-dependent K+ (SDK) channels. Channels with the same properties were maximally activated by patch excision, suggesting that either an intracellular messenger or interactions with the cytoskeleton regulate open probability. Internal 4-aminopyridine, Ca2+ (10(-8) to 10(-6) M), and tetraethylammonium (internal or external) were without effect on SDK channels. Nitric oxide donors (and cell-permeant cGMP analogues) activated SDK channels, suggesting that these channels may mediate a portion of the enteric inhibitory neural response in colonic muscles. In summary, SDK channels are an important conductance expressed by colonic muscle cells. SDK channels may stabilize membrane potential during dynamic changes in cell length and mediate responses to enteric neurotransmitters.
Figures



References
-
- Brayden JE, Nelson MT. Regulation of arterial tone by activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels. Science. 1992;256:532–535. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G, Prosser CL. Responses of smooth muscles to quick stretch; relation of stretch to conduction. American Journal of Physiology. 1960;198:921–925. - PubMed
-
- Dick GM, Bradley KK, Horowitz B, Hume JR, Sanders KM. Functional and molecular identification of a novel chloride conductance in canine colonic smooth muscle. American Journal of Physiology. 1998;275:C940–950. - PubMed
-
- Farrugia G, Holm AN, Rich A, Sarr MG, Szurszewski JH, Rae JL. A mechanosensitive calcium channel in human intestinal smooth muscle cells. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:900–905. - PubMed
-
- Fay FS. Mechanical propeties of single isolated smooth muscle cells. In: Worcel M, Vassort G, editors. Les Colloques de INSERM: Smooth Muscle Pharmacology and Physiology. Paris: Editions INSERM; 2000. pp. 327–342.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

