Atrial natriuretic factor increases splenic microvascular pressure and fluid extravasation in the rat
- PMID: 11351034
- PMCID: PMC2278622
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0273b.x
Atrial natriuretic factor increases splenic microvascular pressure and fluid extravasation in the rat
Abstract
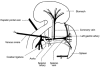
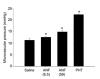
The spleen is an important site of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)-induced fluid extravasation into the systemic lymphatic system. The mechanism underlying this process was studied in a blood-perfused (1 ml min(-1)) rat spleen using the double occlusion technique. To ensure that our observations were spleen specific, a similar protocol was repeated in the hindquarters. Rat ANF(1-28), infused into the splenic artery of anaesthetized male rats, caused a dose-dependent (0.3-59 pmol min(-1)) increase in microvascular pressure from 11.3 +/- 0.7 to 14.9 +/- 0.5 mmHg and in post-capillary resistance from 7.2 +/- 0.6 to 10.1 +/- 1.1 mmHg ml(-1). ANF elicited no change in splenic pre-capillary resistance or in hindquarter haemodynamics. Intrasplenic ANF (6.5 pmol min(-1)) caused a sustained increase in intrasplenic fluid efflux from 0.1 +/- 0.1 to 0.3 +/- 0.1 ml min(-1), and in capillary filtration coefficient (Kf) from 1.2 +/- 0.5 to 2.4 +/- 0.6 ml mmHg-1 min-1 (100 g tissue)-1. Mechanical elevation of splenic intravascular pressure (from 11.3 +/- 0.7 to 22.4 +/- 0.2 mmHg) significantly increased intrasplenic fluid extravasation (from 0.4 +/- 0.3 to 1.4 +/- 0.3 ml min(-1)). The natriuretic peptide receptor-C (NPRC)-specific agonist C-ANF(4-23) (12.5 and 125 pmol min(-1)) did not alter splenic intravascular pressure or pre-/post-capillary resistance. The ANF antagonist A71915 (8.3 and 83 pmol min-1), which blocks ANF-stimulated cGMP production via natriuretic peptide receptor-A (NPRA), inhibited the ANF-induced changes in splenic microvascular pressure and post-capillary resistance. It is concluded that ANF enhances the extravasation of isoncotic fluid from the splenic vasculature both by raising intrasplenic microvascular pressure (increased post-capillary resistance) and by increasing filtration area. The constrictive activity of ANF on the splenic vasculature is mediated through NPRA.
Figures
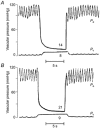
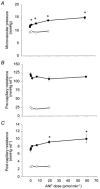
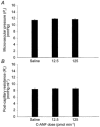
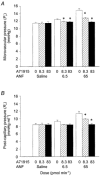
 ; and 83 pmol min−1, ▪) was co-infused with ANF (6.5 and 65 pmol min−1) continuously via the splenic artery. The control animals were infused with isotonic saline (□). The haemodynamic responses were measured at 5, 10 and 20 min using the double occlusion technique. Separate animals were used for each dose (n = 4 for each group). The vertical error bars indicate
; and 83 pmol min−1, ▪) was co-infused with ANF (6.5 and 65 pmol min−1) continuously via the splenic artery. The control animals were infused with isotonic saline (□). The haemodynamic responses were measured at 5, 10 and 20 min using the double occlusion technique. Separate animals were used for each dose (n = 4 for each group). The vertical error bars indicate Similar articles
-
Adrenomedullin increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat.J Physiol. 2001 Jul 15;534(Pt. 2):527-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00527.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11454969 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of portal hypertension on splenic blood flow, intrasplenic extravasation and systemic blood pressure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003 Jun;284(6):R1580-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00516.2002. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12736184
-
Influence of atrial natriuretic factor on fluid efflux from the splenic circulation of the rat.J Physiol. 1996 Feb 15;491 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):225-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021210. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 9011615 Free PMC article.
-
Role of spleen in integrated control of splanchnic vascular tone: physiology and pathophysiology.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;87(1):1-7. doi: 10.1139/Y08-103. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19142210 Review.
-
Atrial natriuretic factor and its role in the regulation of electrolyte, volume and pressure homeostasis.Czech Med. 1989;12(1):1-21. Czech Med. 1989. PMID: 2524370 Review.
Cited by
-
Constriction of rat extra-splenic veins to lipopolysaccharide involves endothelin-1.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;381(6):555-62. doi: 10.1007/s00210-010-0514-9. Epub 2010 Apr 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20397012
-
Right Heart Failure and Cardiorenal Syndrome.Cardiol Clin. 2020 May;38(2):185-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2020.01.004. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Cardiol Clin. 2020. PMID: 32284096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Social Isolation During Prolonged Simulated Weightlessness by Hindlimb Unloading.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 13;10:1147. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01147. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31572207 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelium is critically involved in the hypotensive and hypovolemic actions of atrial natriuretic peptide.J Clin Invest. 2005 Jun;115(6):1666-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI23360. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15931395 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat.J Physiol. 2001 Jul 15;534(Pt. 2):527-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00527.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11454969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand-Srivastava MB, Trachte GJ. Atrial natriuretic factor receptors and signal transduction mechanisms. Pharmacological Reviews. 1993;45:455–497. - PubMed
-
- Atlas SA, Volpe M, Sosa RE, Laragh JH, Camargo MJF, Maack T. Effect of atrial natriuretic factor on blood pressure and the renin angiotensin aldosterone system. Federation Proceedings. 1986;45:2115–2121. - PubMed
-
- Barclay PL, Bennett JA, Greengrass PM, Griffin A, Samuels GMR, Sheperson NB. The pharmacokinetics of I-125-atrial natriuretic factor in anaesthetized rats - effects of neutral endopeptidase inhibition with candoxatrilat and of ANF-C receptor blockade. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1992;44:1013–1022. - PubMed
-
- Barman SA. Role of calcium-activated potassium channels and cyclic nucleotides on pulmonary vasoreactivity to serotonin. American Journal of Physiology. 1997;273:142–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

