Synergism of Xist RNA, DNA methylation, and histone hypoacetylation in maintaining X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 11352938
- PMCID: PMC2192370
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.4.773
Synergism of Xist RNA, DNA methylation, and histone hypoacetylation in maintaining X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
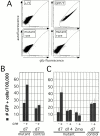
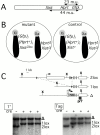
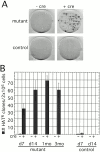
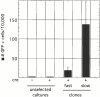
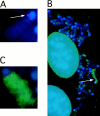
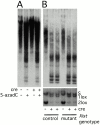
Xist RNA expression, methylation of CpG islands, and hypoacetylation of histone H4 are distinguishing features of inactive X chromatin. Here, we show that these silencing mechanisms act synergistically to maintain the inactive state. Xist RNA has been shown to be essential for initiation of X inactivation, but not required for maintenance. We have developed a system in which the reactivation frequency of individual X-linked genes can be assessed quantitatively. Using a conditional mutant Xist allele, we provide direct evidence for that loss of Xist RNA destabilizes the inactive state in somatic cells, leading to an increased reactivation frequency of an X-linked GFP transgene and of the endogenous hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (Hprt) gene in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Demethylation of DNA, using 5-azadC or by introducing a mutation in Dnmt1, and inhibition of histone hypoacetylation using trichostatin A further increases reactivation in Xist mutant fibroblasts, indicating a synergistic interaction of X chromosome silencing mechanisms.
Figures
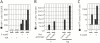
References
-
- Barr M.L., Carr D.H. Correlation between sex chromatin and chromosomes. Acta Cytol. 1962;6:34–45. - PubMed
-
- Borsani G., Tonlorenzi R., Simmler M.C., Dandolo L., Arnaud D., Capra V., Grompe M., Pizzuti A., Muzny D., Lawrence C. Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;351:325–329. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N., Ashworth A., Kay G.F., Cooper P., Smith S., McCabe V.M., Norris D.P., Penny G.D., Patel D., Rastan S. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse Xist from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;351:329–331. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N., Ashworth A., Kay G.F., McCabe V.M., Norris D.P., Cooper P.J., Swift S., Rastan S. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15-kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell. 1992;71:515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

