A central role for the armadillo protein plakoglobin in the autoimmune disease pemphigus vulgaris
- PMID: 11352942
- PMCID: PMC2192383
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.4.823
A central role for the armadillo protein plakoglobin in the autoimmune disease pemphigus vulgaris
Abstract
In pemphigus vulgaris (PV), autoantibody binding to desmoglein (Dsg) 3 induces loss of intercellular adhesion in skin and mucous membranes. Two hypotheses are currently favored to explain the underlying molecular mechanisms: (a) disruption of adhesion through steric hindrance, and (b) interference of desmosomal cadherin-bound antibody with intracellular events, which we speculated to involve plakoglobin. To investigate the second hypothesis we established keratinocyte cultures from plakoglobin knockout (PG-/-) embryos and PG+/+ control mice. Although both cell types exhibited desmosomal cadherin-mediated adhesion during calcium-induced differentiation and bound PV immunoglobin (IgG) at their cell surface, only PG+/+ keratinocytes responded with keratin retraction and loss of adhesion. When full-length plakoglobin was reintroduced into PG-/- cells, responsiveness to PV IgG was restored. Moreover, in these cells like in PG+/+ keratinocytes, PV IgG binding severely affected the linear distribution of plakoglobin at the plasma membrane. Taken together, the establishment of an in vitro model using PG+/+ and PG-/- keratinocytes allowed us (a) to exclude the steric hindrance only hypothesis, and (b) to demonstrate for the first time that plakoglobin plays a central role in PV, a finding that will provide a novel direction for investigations of the molecular mechanisms leading to PV, and on the function of plakoglobin in differentiating keratinocytes.
Figures
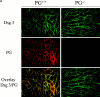








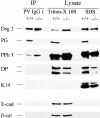




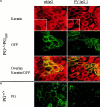
References
-
- Amagai M. Adhesion molecules. IKeratinocyte-keratinocyte interactions; cadherins and pemphigus. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1995;104:146–152. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M., Komai A., Hashimoto T., Shirakata Y., Hashimoto K., Yamada T., Kitajima Y., Ohya K., Iwanami H., Nishikawa T. Usefulness of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant desmogleins 1 and 3 for serodiagnosis of pemphigus. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999;140:351–357. - PubMed
-
- Anhalt G.J., Labib R.S., Voorhees J.J., Beals T.F., Diaz L.A. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982;306:1189–1196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

