Antisense oligonucleotides selected by hybridisation to scanning arrays are effective reagents in vivo
- PMID: 11353073
- PMCID: PMC55457
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.10.2041
Antisense oligonucleotides selected by hybridisation to scanning arrays are effective reagents in vivo
Abstract
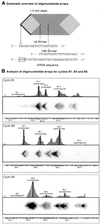
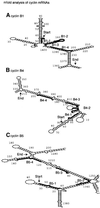
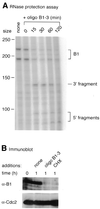
Transcripts representing mRNAs of three Xenopus cyclins, B1, B4 and B5, were hybridised to arrays of oligonucleotides scanning the first 120 nt of the coding region to assess the ability of the immobilised oligonucleotides to form heteroduplexes with their targets. Oligonucleotides that produced high heteroduplex yield and others that showed little annealing were assayed for their effect on translation of endogenous cyclin mRNAs in Xenopus egg extracts and their ability to promote cleavage of cyclin mRNAs in oocytes by RNase H. Excellent correlation was found between antisense potency and affinity of oligonucleotides for the cyclin transcripts as measured by the array, despite the complexity of the cellular environment.
Figures




References
-
- Branch A.D. (1998) Antisense drug discovery: can cell-free screens speed the process? Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev., 8, 249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

