Oxacillinase-mediated resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 11353602
- PMCID: PMC90522
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1615-1620.2001
Oxacillinase-mediated resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
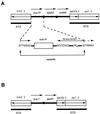
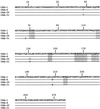
Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate SOF-1 was resistant to cefepime and susceptible to ceftazidime. This resistance phenotype was explained by the expression of OXA-31, which shared 98% amino acid identity with a class D beta-lactamase, OXA-1. The oxa-31 gene was located on a ca. 300-kb nonconjugative plasmid and on a class 1 integron. No additional efflux mechanism for cefepime was detected in P. aeruginosa SOF-1. Resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in P. aeruginosa were conferred by OXA-1 as well.
Figures

References
-
- Chen H Y, Yuan M, Livermore D M. Mechanisms of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics amongst Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates collected in the UK in 1993. J Med Microbiol. 1995;43:300–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

