Selection and characterization of varicella-zoster virus variants resistant to (R)-9-[4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethy)butyl]guanine
- PMID: 11353604
- PMCID: PMC90524
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1629-1636.2001
Selection and characterization of varicella-zoster virus variants resistant to (R)-9-[4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethy)butyl]guanine
Abstract
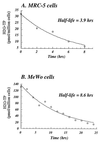
(R)-9-[4-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethy)butyl]guanine (H2G) is a potent and selective inhibitor of herpesvirus replication. It is a nucleoside analog, and its triphosphate derivative (H2G-TP) is a competitive inhibitor of herpesvirus DNA polymerases. In this study, the antiviral activities of H2G and acyclovir (ACV) and the development of viral resistance to these agents were compared in varicella-zoster virus (VZV)-infected cells. In plaque reduction assays, the 50% effective concentration of H2G for VZV was 60- to 400-fold lower than that of ACV, depending on the virus strain and the cell line tested. The enhanced efficacy of H2G against VZV can be accounted for in part by the fact that the intaracellular H2G-TP level (>170 pmol/10(6) cells) is higher than the intracellular ACV-TP level (<1 pmol/10(6) cells). In addition, H2G-TP has extended half-lives of 3.9 and 8.6 h in VZV-infected MRC-5 and MeWo cells, respectively. To assess the emergence of H2G-resistant VZV in vitro, VZV was passaged in the presence of increasing concentrations of H2G. Earlier in the passage, when the concentration of H2G was relatively low, the predominant variant had the (A)76 deletion in the viral thymidine kinase (TK) gene. This mutant was identical to an ACV-resistant mutant generated in parallel experiments. However, higher concentrations of H2G appeared to favor a novel mutant, which had deletions of two consecutive nucleotides at positions 805 and 806 of the TK gene. All of these changes introduced frameshift mutations in the TK gene resulting in the expression of truncated polypeptides. H2G-resistant viruses were cross-resistant to ACV, and vice versa.
Figures

References
-
- Abele G, Cox S, Bergman S, Lindborg B, Vissgarden A, Karlstrom A, Harmenberg J, Wahren B. Antiviral activity against VZV and HSV type 1 and type 2 of the (+) and (−) enantiomers of (R,S)-9-[4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)butyl]guanine, in comparison to other closely related acyclic nucleosides. Antivir Chem Chemother. 1991;2:163–169.
-
- Andrei G, Snoeck R, Reymen D, Liesnard C, Goubau P, Desmyter J, De Clercq E. Comparative activity of selected antiviral compounds against clinical isolates of varicella-zoster virus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;14:318–328. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

