Genotypic and phenotypic resistance patterns of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants with insertions or deletions in the reverse transcriptase (RT): multicenter study of patients treated with RT inhibitors
- PMID: 11353634
- PMCID: PMC90554
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1836-1842.2001
Genotypic and phenotypic resistance patterns of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants with insertions or deletions in the reverse transcriptase (RT): multicenter study of patients treated with RT inhibitors
Abstract
Genomic rearrangements in the 5' part of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) have been involved in multidrug resistance to nucleoside RT inhibitors (NRTI). We carried out a retrospective, multicenter study to investigate the prevalence, variability, and phenotypic consequences of such rearrangements. Data concerning the HIV-1 RT genotype and the biological and clinical characteristics of NRTI-treated patients were collected from 10 virology laboratories. Sensitivities of the different HIV-1 variants to RT inhibitors were analyzed in a single-cycle recombinant virus assay. Fifty-two of 2,152 (2.4%) RT sequences had a rearrangement in the 5' part of the RT, with an extensive molecular variation. The number of codons inserted between positions 68 and 69 ranged from 1 (3 samples) or 2 (41 samples) to 5 and 11 in one case each. In four cases, codon 67 was deleted. High levels of phenotypic resistance to zidovudine (AZT), lamivudine (3TC), stavudine (d4T), abacavir (ABC), and didanosine (ddI) were found in 95, 92, 72, 62, and 15% of the 40 samples analyzed, respectively. Resistance to AZT, d4T, and ABC could be found in the absence of the T215Y/F mutations. Resistance to 3TC could develop in the absence of specific mutations. Low-level resistance to ddI was noticed in 40% of the patients. The deletions of codon 67 seemed to have little effect on NRTI sensitivity. Most of the rearrangements were shown to contribute to cross-resistance to NRTI. The results regarding susceptibility to ddI raise the question of the interpretation of the phenotypic data concerning this drug.
Figures
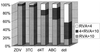
References
-
- Balotta C, Violin M, Monno L, Bagnarelli P, Riva C, Facchi G, Berlusconi A, Lippi M, Rusconi S, Clementi M, Galli M, Angarano G, Moroni M. Prevalence of multiple dideoxynucleoside analogue resistance (MddNR) in a multicenter cohort of HIV-1-infected Italian patients with virologic failure. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000;24:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Boucher C A B, O'Sullivan E, Mulder J W, Ramautarsing C, Kellam P, Darby G, Lange J M A, Goudsmit J, Larder B A. Ordered appearance of zidovudine resistance mutations during treatment of 18 human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Charneau P, Mirambeau G, Roux P, Paulous S, Buc H, Clavel F. HIV-1 reverse transcription: a termination step at the centre of the genome. J Mol Biol. 1994;241:651–662. - PubMed
-
- Chou T-C. The median-effect principle and the combination index for quantitation of synergism and antagonism, P. 61–102. In: Chou T-C, Rideout J, editors. Synergism and antagonism in chemotherapy. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1991.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

