Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of linezolid following multiple oral doses
- PMID: 11353635
- PMCID: PMC90555
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1843-1846.2001
Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of linezolid following multiple oral doses
Abstract
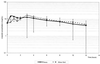
The pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose linezolid were determined following administration of five 600-mg oral doses given every 12 h to each of six healthy male volunteers. Concentrations of the drug were determined in plasma and inflammatory blister fluid using high-pressure liquid chromatography. A mean peak concentration in plasma of 18.3 microg/ml (standard deviation [SD], 6.0) was attained at a mean time of 0.7 h (SD, 0.3) after the final dose. The penetration into the inflammatory fluid was 104% (SD, 20.7). A mean peak concentration of 16.4 microg/ml (SD, 10.6) was attained in the inflammatory fluid at 3 h (SD, 0.6) after the final dose. The elimination half-life from serum and inflammatory fluid was 4.9 (SD, 1.8) and 5.7 (SD, 1.7) h, respectively. The area under the concentration-time curve in plasma and blister fluid was 140.3 (SD, 73.1) and 155.3 (SD, 80.1) microg x h/ml, respectively. These data suggest that linezolid has good tissue penetration, and we can predict that it will be successful in the treatment of a variety of gram-positive infections.
Figures
References
-
- Ford C, Hamel J, Stapert D, Moerman J, Hutchinson H, Barbachyn M, Zurenko G. Oxazolidinones: a new class of antimicrobials. Infect Med. 1999;16:435–445.
-
- Hyatt J M, McKinnon P S, Zimmer G S, Schentag J J. The importance of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic surrogate markers of outcome. Focus on antibacterial agents. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995;28:143–160. - PubMed
-
- Lasher-Sisson T, Jungbluth G, Hopkins N K. A pharmacokinetic evaluation of concomitant administration of linezolid and aztreonam. J Clin Pharmacol. 1999;39:1277–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases