CENTA as a chromogenic substrate for studying beta-lactamases
- PMID: 11353639
- PMCID: PMC90559
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1868-1871.2001
CENTA as a chromogenic substrate for studying beta-lactamases
Abstract
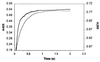
CENTA, a chromogenic cephalosporin, is readily hydrolyzed by beta-lactamases of all classes except for the Aeromonas hydrophila metalloenzyme. Although it cannot practically be used for the detection of beta-lactamase-producing strains on agar plates, it should be quite useful for kinetic studies and the detection of the enzymes in crude extracts and chromatographic fractions.
Figures
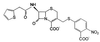
References
-
- Bouillenne F, Matagne A, Joris B, Frère J-M. Technique for a rapid and efficient purification of the SHV-1 and PSE-2 beta-lactamases. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000;737:261–265. - PubMed
-
- De Meester F, Joris B, Reckinger G, Bellefroid-Bourguignon C, Frère J M, Waley S G. Automated analysis of enzyme inactivation phenomena. Application to beta-lactamases and dd-peptidases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;36:2393–2403. - PubMed
-
- Faraci W S, Pratt R F. Mechanism of inhibition of the PC1 beta-lactamase of Staphylococcus aureus by cephalosporins: importance of the 3′-leaving group. Biochemistry. 1985;24:903–910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

