Azithromycin inhibits quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 11353657
- PMCID: PMC90577
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1930-1933.2001
Azithromycin inhibits quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
We report that 2 microg of azithromycin/ml inhibits the quorum-sensing circuitry of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1. Addition of synthetic autoinducers partially restored the expression of the trancriptional activator-encoding genes lasR and rhlR but not that of the autoinducer synthase-encoding gene lasI. We propose that azithromycin interferes with the synthesis of autoinducers, by an unknown mechanism, leading to a reduction of virulence factor production.
Figures
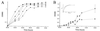
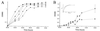


References
-
- Akrim M, Bally M, Ball G, Tommassen J, Teerink H, Filloux A, Lazdunski A. Xcp-mediated protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of two additional genes and evidence for regulation of xcp gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993;10:431–443. - PubMed
-
- Bally M, Filloux A, Akrim M, Ball G, Lazdunski A, Tommassen J. Protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: characterization of seven xcp genes and processing of secretory apparatus components by prepilin peptidase. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:1121–1131. - PubMed
-
- Chapon V, Akrim M, Latifi A, Williams P, Lazdunski A, Bally M. Regulation of the xcp secretion pathway by multiple quorum-sensing modulons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:1169–1178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

