Impact of interferon therapy on the natural history of hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis
- PMID: 11358906
- PMCID: PMC1728334
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.48.6.843
Impact of interferon therapy on the natural history of hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: The role of interferon treatment on the natural history of hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis is under debate.
Aim: To evaluate the effect of interferon on the clinical course of compensated hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis.
Patients and methods: Seventy two cirrhotic patients treated with interferon and 72 untreated controls matched treated patients with for quinquennia of age, sex, and Child-Pugh's score were enrolled in a prospective non-randomised controlled trial. Treated patients received leucocytic interferon alfa, with an escalating schedule for 12 months. The incidence and risk (Cox regression analysis) of clinical complications (hepatocellular carcinoma, ascites, jaundice, variceal bleeding, and encephalopathy) and death were calculated.
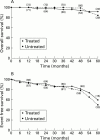
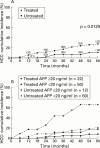
Results: Over median follow up periods of 55 months for treated and 58 for untreated subjects, seven and nine patients, respectively, died, and 20 and 32, respectively, developed at least one clinical complication (ns). Hepatocellular carcinoma developed in six treated and 19 untreated patients (p=0.018). Seven treated patients showed sustained aminotranferase normalisation and none died or developed complications. Clinical complications were significantly associated with low albumin, bilirubin, and prothrombin activity while hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly related to no treatment with interferon, oesophageal varices, and high alpha fetoprotein levels. By stratified analysis, the beneficial effect of interferon was statistically evident only in patients with baseline alpha fetoprotein levels > or =20 ng/ml.
Conclusions: Interferon does not seem to affect overall or event free survival of patients with hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis while it seems to prevent the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Patients who achieved sustained aminotransferase normalisation survived and did not develop any complications during follow up.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
