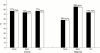Impact of hypertension on the accuracy of exercise stress myocardial perfusion imaging for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 11359747
- PMCID: PMC1729751
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.85.6.655
Impact of hypertension on the accuracy of exercise stress myocardial perfusion imaging for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease
Abstract
Aim: To compare the accuracy of exercise stress myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease in patients with and without hypertension.
Methods: A symptom limited bicycle exercise stress test in conjunction with 99m technetium sestamibi or tetrofosmin SPECT imaging was performed in 332 patients (mean (SD) age, 57 (10) years; 257 men, 75 women) without previous myocardial infarction who underwent coronary angiography. Of these, 137 (41%) had hypertension. Rest SPECT images were acquired 24 hours after the stress test. An abnormal scan was defined as one with reversible or fixed perfusion defects.
Results: In hypertensive patients, myocardial perfusion abnormalities were detected in 79 of 102 patients with significant coronary artery disease and in nine of 35 patients without. In normotensive patients, myocardial perfusion abnormalities were detected in 104 of 138 patients with significant coronary artery disease and in 16 of 57 patients without. There were no differences between normotensive and hypertensive patients in sensitivity (77% (95% confidence interval (CI) 69% to 86%) v 75% (95% CI 68% to 83%)), specificity (74% (95% CI 60% to 89%) v 72% (95% CI 60% to 84%)), and accuracy (77% (95% CI 70% to 84%) v 74% (95% CI 68% to 80%)) of exercise SPECT for diagnosing coronary artery disease. The accuracy of SPECT was greater than electrocardiography, both in hypertensive patients (p = 0.005) and in normotensive patients (p = 0.0001). For the detection of coronary artery disease in individual vessels, sensitivity was 58% (95% CI 51% to 65%) v 57% (95% CI 51% to 64%), specificity was 86% (95% CI 82% to 90%) v 85% (95% CI 81% to 89%), and accuracy was 74% (95% CI 70% to 78%) v 74% (95% CI 70% to 78%) in patients with and without hypertension (NS).
Conclusions: In the usual clinical setting, the value of exercise myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for diagnosing coronary artery disease is not degraded by the presence of hypertension.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous