Sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by 6-hydroxydopamine: implications for Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 11359871
- PMCID: PMC1868550
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00304.x
Sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by 6-hydroxydopamine: implications for Parkinson's disease
Abstract
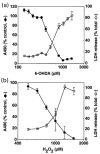
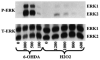
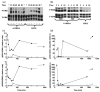
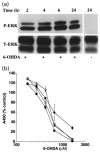
Although the toxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is utilized extensively in animal models of Parkinson's disease, the underlying mechanism of its toxic effects on dopaminergic neurons is not completely understood. We examined the effects of 6-OHDA on the CNS-derived tyrosine hydroxylase expressing B65 cell line, with particular attention to the regulation of the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK). 6-OHDA elicited a dose-dependent cytotoxicity in B65 cells. Toxic doses of 6-OHDA also elicited a biphasic pattern of ERK phosphorylation with a prominent sustained phase, a pattern that differed from that observed with hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) treatment. 6-OHDA-elicited ERK phosphorylation was blocked by PD98059, an inhibitor of the upstream mitogen activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) that phosphorylates and activates ERK. PD98059 also conferred protection against 6-OHDA cytotoxicity, but did not affect H(2)O(2) toxicity in B65 cells. These results suggest that ERK activation plays a direct mechanistic role in 6-OHDA toxicity, rather than representing a protective compensatory response, and raise the possibility that abnormal patterns of ERK activation may contribute to dopaminergic neuronal cell death.
Figures

References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Ambani LM, Van Woert MH, Murphy S. Brain peroxidase and catalase in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 1975;32:114–118. - PubMed
-
- Andrew R, Watson DG, Best SA, Midgley JM, Wenlong H, Petty RKH. The determination of hydroxydopamines and other trace amines in the urine of Parkinsonian patients and normal controls. Neurochem Res. 1993;18:1175–1177. - PubMed
-
- Asanuma M, Hirata H, Cadet JL. Attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic nigrostriatal lesions in superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Neuroscience. 1998;85:907–917. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Aging, energy, and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:357–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

