HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression
- PMID: 11359907
- PMCID: PMC87062
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.3995-4004.2001
HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression
Abstract
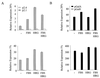
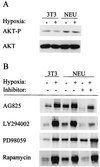
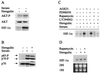
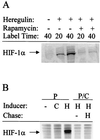
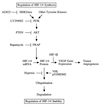
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a transcriptional activator composed of HIF-1alpha and HIF-1beta subunits. Several dozen HIF-1 targets are known, including the gene encoding vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1alpha expression increases as a result of decreased ubiquitination and degradation. The tumor suppressors VHL (von Hippel-Lindau protein) and p53 target HIF-1alpha for ubiquitination such that their inactivation in tumor cells increases the half-life of HIF-1alpha. Increased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and AKT or decreased PTEN activity in prostate cancer cells also increases HIF-1alpha expression by an undefined mechanism. In breast cancer, increased activity of the HER2 (also known as neu) receptor tyrosine kinase is associated with increased tumor grade, chemotherapy resistance, and decreased patient survival. HER2 has also been implicated as an inducer of VEGF expression. Here we demonstrate that HER2 signaling induced by overexpression in mouse 3T3 cells or heregulin stimulation of human MCF-7 breast cancer cells results in increased HIF-1alpha protein and VEGF mRNA expression that is dependent upon activity of PI3K, AKT (also known as protein kinase B), and the downstream kinase FRAP (FKBP-rapamycin-associated protein). In contrast to other inducers of HIF-1 expression, heregulin stimulation does not affect the half-life of HIF-1alpha but instead stimulates HIF-1alpha synthesis in a rapamycin-dependent manner. The 5'-untranslated region of HIF-1alpha mRNA directs heregulin-inducible expression of a heterologous protein. These data provide a molecular basis for VEGF induction and tumor angiogenesis by heregulin-HER2 signaling and establish a novel mechanism for the regulation of HIF-1alpha expression.
Figures
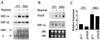



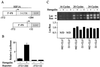
References
-
- Aebersold D M, Burri P, Beer K T, Laissue J, Djonov V, Greiner R H, Semenza G L. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a: a novel predictive and prognostic parameter in the radiotherapy of oropharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2911–2916. - PubMed
-
- Agani F, Semenza G L. Mersalyl is a novel inducer of vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:749–754. - PubMed
-
- Bagheri-Yarmand R, Vadlamudi R K, Wang R A, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Vascular endothelial growth factor upregulation via p21-activated kinase-1 signaling regulates heregulin-β1-mediated angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39451–39457. - PubMed
-
- Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Plank C, Breitenecker G, Oberhuber G. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is a marker for an unfavorable prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4693–4696. - PubMed
-
- Bos R, Zhong H, Hanrahan C F, Mommers E C M, Semenza G L, Pinedo H M, Abeloff M D, Simons J W, van Diest P J, van der Wall E. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α during breast carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;93:309–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
