Impaired DNA damage response in cells expressing an exon 11-deleted murine Brca1 variant that localizes to nuclear foci
- PMID: 11359908
- PMCID: PMC87063
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.4005-4015.2001
Impaired DNA damage response in cells expressing an exon 11-deleted murine Brca1 variant that localizes to nuclear foci
Abstract
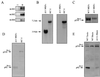
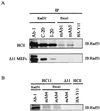
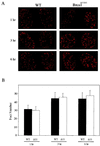
Both human and mouse cells express an alternatively spliced variant of BRCA1, BRCA1-Delta11, which lacks exon 11 in its entirety, including putative nuclear localization signals. Consistent with this, BRCA1-Delta11 has been reported to reside in the cytoplasm, a localization that would ostensibly preclude it from playing a role in the nuclear processes in which its full-length counterpart has been implicated. Nevertheless, the finding that murine embryos bearing homozygous deletions of exon 11 survive longer than embryos that are homozygous for Brca1 null alleles suggests that exon 11-deleted isoforms may perform at least some of the functions of Brca1. We have analyzed both the full-length and the exon 11-deleted isoforms of the murine Brca1 protein. Our results demonstrate that full-length murine Brca1 is identical to human BRCA1 with respect to its cell cycle regulation, DNA damage-induced phosphorylation, nuclear localization, and association with Rad51. Surprisingly, we show that endogenous Brca1-Delta11 localizes to discrete nuclear foci indistinguishable from those found in wild-type cells, despite the fact that Brca1-Delta11 lacks previously defined nuclear localization signals. However, we further show that DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of Brca1-Delta11 is significantly reduced compared to full-length Brca1, and that gamma irradiation-induced Rad51 focus formation is impaired in cells in which only Brca1-Delta11 is expressed. Our results suggest that the increased viability of embryos bearing homozygous deletions of exon 11 may be due to expression of Brca1-Delta11 and suggest an explanation for the genomic instability that accompanies the loss of full-length Brca1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impaired meiotic DNA-damage repair and lack of crossing-over during spermatogenesis in BRCA1 full-length isoform deficient mice.Development. 2003 May;130(9):2001-12. doi: 10.1242/dev.00410. Development. 2003. PMID: 12642502
-
Haploinsufficiency of Parp1 accelerates Brca1-associated centrosome amplification, telomere shortening, genetic instability, apoptosis, and embryonic lethality.Cell Death Differ. 2007 May;14(5):924-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402105. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Cell Death Differ. 2007. PMID: 17318223
-
Normal lymphocyte development and thymic lymphoma formation in Brca1 exon-11-deficient mice.Oncogene. 2003 Jan 30;22(4):528-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206208. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12555066
-
Localization of BRCA1 protein at the cellular level.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998 Oct;3(4):423-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1018740216630. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1998. PMID: 10819536 Review.
-
The function of BRCA1 in DNA damage response.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2000;65:547-52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2000.65.547. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2000. PMID: 12760072 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The functional role of the novel biomarker karyopherin α 2 (KPNA2) in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Apr 30;331(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.12.013. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23268335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRCA1 pathway function in basal-like breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;34(20):3828-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01646-13. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25092866 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Oct;2(10):a003236. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003236. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20719876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Declining BRCA-Mediated DNA Repair in Sperm Aging and its Prevention by Sphingosine-1-Phosphate.Reprod Sci. 2020 Mar;27(3):940-953. doi: 10.1007/s43032-019-00098-1. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Reprod Sci. 2020. PMID: 31916095 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1 is an essential regulator of heart function and survival following myocardial infarction.Nat Commun. 2011 Dec 20;2:593. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1601. Nat Commun. 2011. PMID: 22186889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott D W, Thompson M E, Robinson-Benion C, Tomlinson G, Jensen R A, Holt J T. BRCA1 expression restores radiation resistance in BRCA1-defective cancer cells through enhancement of transcription-coupled DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18808–18812. - PubMed
-
- Anderson S F, Schlegel B P, Nakajima T, Wolpin E S, Parvin J D. BRCA1 protein is linked to the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex via RNA helicase A. Nat Genet. 1998;19:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Bachelier R, Dalla Venezia N, Mazoyer S, Frappart L, Lenoir G M, Vincent A. Differential expression and subcellular localization of murine BRCA1 and BRCA1-delta11 isoforms in murine and human cell lines. Int J Cancer. 2000;88:519–524. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Ear U S, Koller B H, Weichselbaum R R, Bishop D K. The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:23899–23903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
