Phospholipase D activity is required for actin stress fiber formation in fibroblasts
- PMID: 11359912
- PMCID: PMC87067
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.4055-4066.2001
Phospholipase D activity is required for actin stress fiber formation in fibroblasts
Abstract
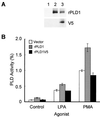
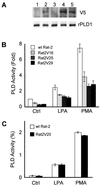
Phospholipase D (PLD) is a ubiquitously expressed enzyme of ill-defined function. In order to explore its cellular actions, we inactivated the rat PLD1 (rPLD1) isozyme by tagging its C terminus with a V5 epitope (rPLD1-V5). This was stably expressed in Rat-2 fibroblasts to see if it acted as a dominant-negative mutant for PLD activity. Three clones that expressed rPLD1-V5 were selected (Rat2V16, Rat2V25, and Rat2V29). Another clone (Rat2V20) that lost expression of rPLD1-V5 was also obtained. In the three clones expressing rPLD1-V5, PLD activity stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) was reduced by ~50%, while the PLD activity of Rat2V20 cells was normal. Changes in the actin cytoskeleton in response to LPA or PMA were examined in these clones. All three clones expressing rPLD1-V5 failed to form actin stress fibers after treatment with LPA. However, Rat2V20 cells formed stress fibers in response to LPA to the same extent as wild-type Rat-2 cells. In contrast, there was no significant change in membrane ruffling induced by PMA in the cells expressing rPLD1-V5. Since Rho is an activator both of rPLD1 and stress fiber formation, the activation of Rho was monitored in wild-type Rat-2 cells and Rat2V25 cells, but no significant difference was detected. The phosphorylation of vimentin mediated by Rho-kinase was also intact in Rat2V25 cells. Rat2V25 cells also showed normal vinculin-containing focal adhesions. However, the translocation of alpha-actinin to the cytoplasm and to the detergent-insoluble fraction in Rat2V25 cells was reduced. These results indicate that PLD activity is required for LPA-induced rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton to form stress fibers and that PLD might be involved in the cross-linking of actin filaments mediated by alpha-actinin.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phospholipase D is associated in a phorbol ester-dependent manner with protein kinase C-alpha and with a 220-kDa protein which is phosphorylated on serine and threonine.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jul 30;248(3):533-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8990. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. PMID: 9703960
-
FGF-2 induced reorganization and disruption of actin cytoskeleton through PI 3-kinase, Rho, and Cdc42 in corneal endothelial cells.Mol Vis. 2003 Dec 8;9:624-34. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 14685150
-
Definition of the protein kinase C interaction site of phospholipase D.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Mar 17;244(2):364-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8275. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. PMID: 9514932
-
A nuclear MAL-function links Rho to SRF.Mol Cell. 2003 May;11(5):1121-3. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00189-8. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12769835 Review.
-
Inter-regulatory dynamics of phospholipase D and the actin cytoskeleton.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep;1791(9):856-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.04.008. Epub 2009 May 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19422932 Review.
Cited by
-
iPLA2beta: front and center in human monocyte chemotaxis to MCP-1.J Exp Med. 2008 Feb 18;205(2):347-59. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071243. Epub 2008 Jan 21. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18208975 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian phospholipase D: Function, and therapeutics.Prog Lipid Res. 2020 Apr;78:101018. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2019.101018. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 31830503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MARCKS and MARCKS-like proteins in development and regeneration.J Biomed Sci. 2018 May 22;25(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0445-1. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29788979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phagocyte cell migration is mediated by phospholipases PLD1 and PLD2.Blood. 2006 Nov 15;108(10):3564-72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-005959. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16873675 Free PMC article.
-
Direct stimulation of receptor-controlled phospholipase D1 by phospho-cofilin.EMBO J. 2007 Oct 3;26(19):4189-202. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601852. Epub 2007 Sep 13. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17853892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Maatsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Bi K, Roth M G, Ktistakis N T. Phosphatidic acid formation by phospholipase D is required for transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Curr Biol. 1997;7:301–307. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard A, Ohanian V, Critchley D. The structure and function of α-actinin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989;10:280–289. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch G M, Bohl B P, Chuang T-H. Guanine nucleotide exchange regulates membrane translocation of Rac/Rho GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:31674–31679. - PubMed
-
- Bremser M, Nickel W, Schweikert M, Ravazzola M, Amhevdt M, Hughes C A, Sollner T H, Rothman J E, Wieland F T. Coupling of coat assembly and vesicle budding to packaging of putative cargo receptors. Cell. 1999;96:495–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
