Analysis of promoter recognition in vivo directed by sigma(F) of Bacillus subtilis by using random-sequence oligonucleotides
- PMID: 11371526
- PMCID: PMC95239
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3623-3630.2001
Analysis of promoter recognition in vivo directed by sigma(F) of Bacillus subtilis by using random-sequence oligonucleotides
Abstract
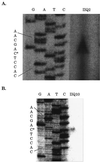
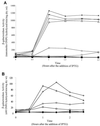
Formation of spores from vegetative bacteria by Bacillus subtilis is a primitive system of cell differentiation. Critical to spore formation is the action of a series of sporulation-specific RNA polymerase sigma factors. Of these, sigma(F) is the first to become active. Few genes have been identified that are transcribed by RNA polymerase containing sigma(F) (E-sigma(F)), and only two genes of known function are exclusively under the control of E-sigma(F), spoIIR and spoIIQ. In order to investigate the features of promoters that are recognized by E-sigma(F), we studied the effects of randomizing sequences for the -10 and -35 regions of the promoter for spoIIQ. The randomized promoter regions were cloned in front of a promoterless copy of lacZ in a vector designed for insertion by double crossover of single copies of the promoter-lacZ fusions into the amyE region of the B. subtilis chromosome. This system made it possible to test for transcription of lacZ by E-sigma(F) in vivo. The results indicate a weak sigma(F)-specific -10 consensus, GG/tNNANNNT, of which the ANNNT portion is common to all sporulation-associated sigma factors, as well as to sigma(A). There was a rather stronger -35 consensus, GTATA/T, of which GNATA is also recognized by other sporulation-associated sigma factors. The looseness of the sigma(F) promoter requirement contrasts with the strict requirement for sigma(A)-directed promoters of B. subtilis. It suggests that additional, unknown, parameters may help determine the specificity of promoter recognition by E-sigma(F) in vivo.
Figures
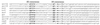
References
-
- Bagyan I, Noback M, Bron S, Paidhungat M, Setlow P. Characterization of yhcN, a new forespore-specific gene of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1998;212:179–188. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera-Hernandez A, Sanchez-Salas J-L, Paidhungat M, Setlow P. Regulation of four genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1999;232:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

