Genetic characterization and evolutionary implications of a car gene cluster in the carbazole degrader Pseudomonas sp. strain CA10
- PMID: 11371531
- PMCID: PMC95244
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3663-3679.2001
Genetic characterization and evolutionary implications of a car gene cluster in the carbazole degrader Pseudomonas sp. strain CA10
Abstract
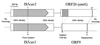
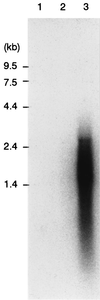
The nucleotide sequences of the 27,939-bp-long upstream and 9,448-bp-long downstream regions of the carAaAaBaBbCAc(ORF7)Ad genes of carbazole-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strain CA10 were determined. Thirty-two open reading frames (ORFs) were identified, and the car gene cluster was consequently revealed to consist of 10 genes (carAaAaBaBbCAcAdDFE) encoding the enzymes for the three-step conversion of carbazole to anthranilate and the degradation of 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate. The high identities (68 to 83%) with the enzymes involved in 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid degradation were observed only for CarFE. This observation, together with the fact that two ORFs are inserted between carD and carFE, makes it quite likely that the carFE genes were recruited from another locus. In the 21-kb region upstream from carAa, aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase genes (ORF26, ORF27, and ORF28) were found. Inductive expression in carbazole-grown cells and the results of homology searching indicate that these genes encode the anthranilate 1,2-dioxygenase involved in carbazole degradation. Therefore, these ORFs were designated antABC. Four homologous insertion sequences, IS5car1 to IS5car4, were identified in the neighboring regions of car and ant genes. IS5car2 and IS5car3 constituted the putative composite transposon containing antABC. One-ended transposition of IS5car2 together with the 5' portion of antA into the region immediately upstream of carAa had resulted in the formation of IS5car1 and ORF9. In addition to the insertion sequence-dependent recombination, gene duplications and presumed gene fusion were observed. In conclusion, through the above gene rearrangement, the novel genetic structure of the car gene cluster has been constructed. In addition, it was also revealed that the car and ant gene clusters are located on the megaplasmid pCAR1.
Figures
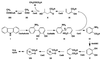


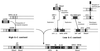
References
-
- Arai H, Yamamoto T, Ohishi T, Shimizu T, Nakata T, Kudo T. Genetic organization and characteristics of the 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid degradation pathway of Comamonas testosteroni TA441. Microbiology. 1999;145:2813–2820. - PubMed
-
- Arcos J C, Argus M F. Molecular geometry and carcinogenic activity of aromatic compounds. New perspectives. Adv Cancer Res. 1968;11:305–471. - PubMed
-
- Avila P, de la Cruz F, Ward E, Grinsted J. Plasmids containing one inverted repeat of Tn21 can fuse with other plasmids in the presence of Tn21 transposase. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195:288–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

