A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis
- PMID: 11375415
- PMCID: PMC209298
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI11871
A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis
Abstract
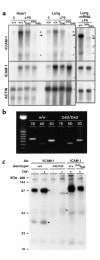
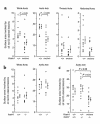
VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 are endothelial adhesion molecules of the Ig gene superfamily that may participate in atherogenesis by promoting monocyte accumulation in the arterial intima. Both are expressed in regions predisposed to atherosclerosis and at the periphery of established lesions, while ICAM-1 is also expressed more broadly. To evaluate functions of VCAM-1 in chronic disease, we disrupted its fourth Ig domain, producing the murine Vcam1(D4D) allele. VCAM-1(D4D) mRNA and protein were reduced to 2-8% of wild-type allele (Vcam1(+)) levels but were sufficient to partially rescue the lethal phenotype of VCAM-1-null embryos. After crossing into the LDL receptor-null background, Vcam1(+/+) and Vcam1(D4D/D4D) paired littermates were generated from heterozygous intercrosses and fed a cholesterol-enriched diet for 8 weeks. The area of early atherosclerotic lesions in the aorta, quantified by en face oil red O staining, was reduced significantly in Vcam1(D4D/D4D) mice, although cholesterol levels, lipoprotein profiles, and numbers of circulating leukocytes were comparable to wild-type. In contrast, deficiency of ICAM-1 either alone or in combination with VCAM-1 deficiency did not alter nascent lesion formation. Therefore, although expression of both VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 is upregulated in atherosclerotic lesions, our data indicate that VCAM-1 plays a dominant role in the initiation of atherosclerosis.
Figures


Comment in
-
VCAM-1 is critical in atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2001 May;107(10):1209-10. doi: 10.1172/JCI13005. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11375406 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

