Ribosome-associated protein that inhibits translation at the aminoacyl-tRNA binding stage
- PMID: 11375931
- PMCID: PMC1083885
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve091
Ribosome-associated protein that inhibits translation at the aminoacyl-tRNA binding stage
Abstract
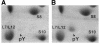
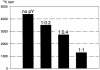
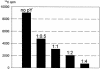
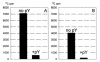
We have recently isolated and characterized a novel protein associated with Escherichia coli ribosomes and named protein Y (pY). Here we show that the ribosomes from bacterial cells growing at a normal physiological temperature contain no pY, whereas a temperature downshift results in the appearance of the protein in ribosomes. The protein also appears in the ribosomes of those cells that reached the stationary phase of growth at a physiological temperature. Our experiments with cell-free translation systems demonstrate that the protein inhibits translation at the elongation stage by blocking the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site. The function of the protein in adaptation of cells to environmental stress is discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Cate J.H., Yusupov, M.M., Yusupova G.Zh., Earnest, T.N. and Noller, H.F. (1999) X-ray crystal structures of 70S ribosome functional complexes. Science, 285, 2095–2104. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie M., Tu, Y., Euskirchen, G., Ward, W.W. and Prasher, D.C. (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science, 263, 802–805. - PubMed
-
- Crameri A., Whitehorn, E.A., Tate, E. and Stemmer, W.P.C. (1996) Improved green fluorescent protein by molecular evolution using DNA shuffling. Nature Biotechnol., 14, 315–319. - PubMed
-
- Dammel C.S. and Noller, H.F. (1995) Suppression of a cold-sensitive mutation in 16S rRNA by overexpression of a novel ribosome-binding factor, RbfA. Genes Dev., 9, 626–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

