Presence of icaA and icaD genes and slime production in a collection of staphylococcal strains from catheter-associated infections
- PMID: 11376050
- PMCID: PMC88104
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.6.2151-2156.2001
Presence of icaA and icaD genes and slime production in a collection of staphylococcal strains from catheter-associated infections
Abstract
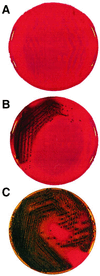
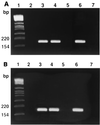
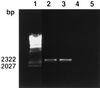
Both Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus are important causes of infections associated with catheters and other medical devices. It has recently been shown that not only S. epidermidis but also S. aureus can produce slime and carries the ica operon responsible for slime production. In the operon, coexpression of icaA and icaD is required for full slime synthesis. In this study, the presence of icaA and icaD was determined in a collection of 91 staphylococcal (68 S. epidermidis and 23 S. aureus) strains from intravenous catheter-associated infections, in 10 strains from the skin and mucosa of healthy volunteers, and in two reference strains by a PCR method. Slime-forming ability was tested on Congo red agar plates; 49% of S. epidermidis strains from catheters and, surprisingly, 61% of S. aureus strains were icaA and icaD positive and slime forming. All the saprophytic strains turned out to be negative for both icaA and icaD and also non-slime forming. Two S. aureus and one S. epidermidis strain from catheters, detected as icaA and icaD positive by PCR analysis and as slime forming (black colonies) at 24 h on Congo red agar, at 48 h exhibited tiny red spikes at the center of black colonies. The onset of these variants could not be ascribed to a mutagenic potential of Congo red, which, in the Ames test, was devoid of mutagenicity. PCR analysis showed that these red variants were negative for both icaA and icaD and even lacking the entire icaADBC operon. The data reported indicate an important role of ica genes as a virulence marker in staphylococcal infections from intravenous catheters.
Figures
Comment in
-
Correlation of Staphylococcus aureus icaADBC genotype and biofilm expression phenotype.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Dec;39(12):4595-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4595-4596.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11797608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ames B, McCann J, Yamasaki E. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Samonella/mammalian microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1975;34:317–364. - PubMed
-
- An Y H, Blair B K, Martin K L, Friedman R J. Macromolecule surface coating for preventing bacterial adhesion. In: An Y H, Friedmann R J, editors. Handbook of bacterial adhesion: principles, methods and applications. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc.; 2000. pp. 609–625.
-
- An Y H, Friedmann R J. Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterial surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998;43:338–348. - PubMed
-
- Arciola C R, Montanaro L, Baldassarri L, Borsetti E, Cavedagna D, Donati M E. Slime production by staphylococci isolated from prosthesis-associated infection. New Microbiol. 1999;22:337–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

