Comparative study using amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting, PCR genotyping, and phenotyping to differentiate Campylobacter fetus strains isolated from animals
- PMID: 11376071
- PMCID: PMC88125
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.6.2283-2286.2001
Comparative study using amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting, PCR genotyping, and phenotyping to differentiate Campylobacter fetus strains isolated from animals
Abstract
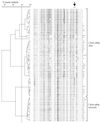
A collection of Campylobacter fetus strains, including both C. fetus subsp. fetus and C. fetus subsp. venerealis, were phenotypically identified to the subspecies level and genotypically typed by PCR and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis. Phenotypic subspecies determination methods were unreliable. Genotyping of the strains by PCR and AFLP showed a clear discrimination between the two subspecies.
Figures
References
-
- Anonymous. OIE manual of standards for diagnostic tests and vaccines 3rd ed. Paris, France: Office International des Epizooties; 1996. pp. 256–266.
-
- Chang W, Ogg J. Transduction and mutation to glycine tolerance in Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971;32:649–653. - PubMed
-
- Denes A S, Lutze-Wallace C L, Cormier M L, Garcia M M. DNA fingerprinting of Campylobacter fetus using cloned constructs of ribosomal RNA and surface array protein genes. Vet Microbiol. 1997;54:185–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

