Spatial-temporal structures of human alpha rhythms: theory, microcurrent sources, multiscale measurements, and global binding of local networks
- PMID: 11376500
- PMCID: PMC6872048
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.1030
Spatial-temporal structures of human alpha rhythms: theory, microcurrent sources, multiscale measurements, and global binding of local networks
Abstract
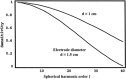
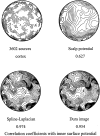
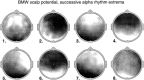
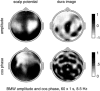
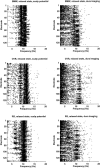
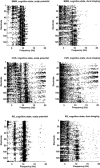
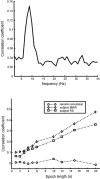
A theoretical framework supporting experimental measures of dynamic properties of human EEG is proposed with emphasis on distinct alpha rhythms. Robust relationships between measured dynamics and cognitive or behavioral conditions are reviewed, and proposed physiological bases for EEG at cellular levels are considered. Classical EEG data are interpreted in the context of a conceptual framework that distinguishes between locally and globally dominated dynamic processes, as estimated with coherence or other measures of phase synchronization. Macroscopic (scalp) potentials generated by cortical current sources are described at three spatial scales, taking advantage of the columnar structure of neocortex. New EEG data demonstrate that both globally coherent and locally dominated behavior can occur within the alpha band, depending on narrow band frequency, spatial measurement scale, and brain state. Quasi-stable alpha phase structures consistent with global standing waves are observed. At the same time, alpha and theta phase locking between cortical regions during mental calculations is demonstrated, consistent with neural network formation. The brain-binding problem is considered in the context of EEG dynamic behavior that generally exhibits both of these local and global aspects. But specific experimental designs and data analysis methods may severely bias physiological interpretations in either local or global directions.
Copyright 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
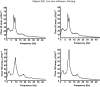

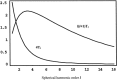
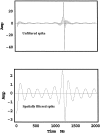
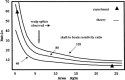




References
-
- Abeles M (1982): Local cortical circuits. New York: Springer‐Verlag.
-
- Abraham K, Ajmone‐Marsan C (1958): Patterns of cortical discharges and their relation to routine scalp electroencephalography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 10: 447–461. - PubMed
-
- Andrew C, Pfurtscheller G (1996): Event‐related coherence as a tool for studying dynamic interaction of brain regions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 98: 144–148. - PubMed
-
- Andrew C, Pfurtscheller G (1997): On the existence of different alpha band rhythms in the hand area of man. Neurosci Lett 222: 103–106. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni F, Babiloni C, Carducci F, Fattorini L, Onorati P, Urbano A (1996): Spline Laplacian estimate of EEG potentials over a realistic magnetic resonance‐constructed scalp surface model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 98: 204–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

